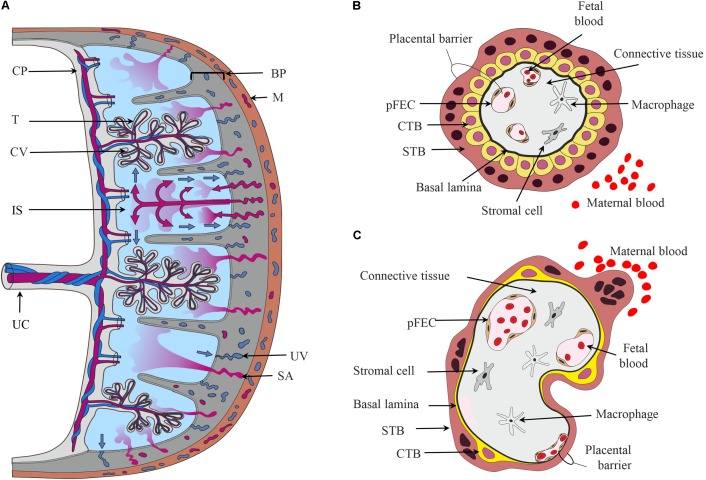
FIGURE 1.
The placental barrier. (A) Schematic depiction of the main structural elements of the human placenta. From the chorionic plate (CP), the umbilical cord (UC), and the chorionic villi (CV) originate. The umbilical vein carries oxygen- and nutrient-rich blood from the placenta to the fetus, while two arteries transport deoxygenated blood and waste products from the fetus to the placenta. The intervillous space (IS) is filled with maternal blood that enters this cavity via remodeled and opened maternal spiral arteries (SA) and leaves via uterine veins (UV). Cells in direct contact with maternal blood are the villous trophoblasts (T). The basal plate (BP) contains extravillous trophoblasts and decidual cells. (B,C) Schematic representation of first trimester (B) and term trimester chorionic villi (C) depicting the major cell types and the placental barrier. CTB, cytotrophoblast; M, myometrium of the maternal uterus, pFECs, placental-fetal endothelial cells; STB, syncytiotrophoblast.