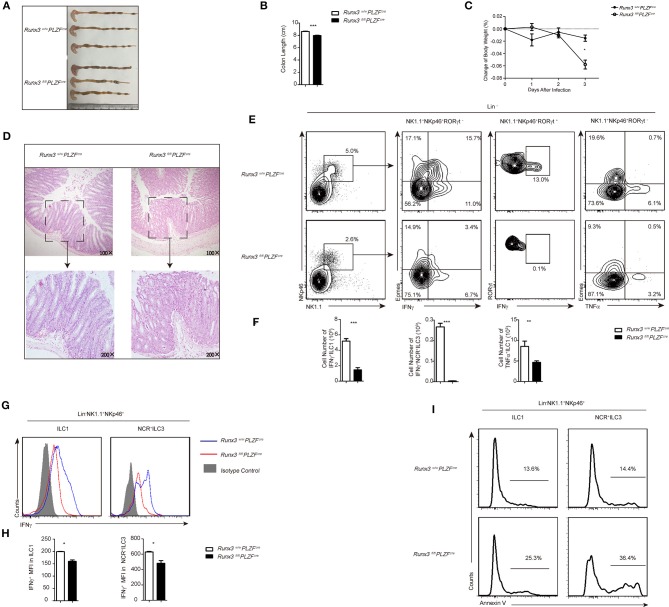
Figure 3.
Defective function of ILC1s and NCR+ILC3s resulted in sensitivity to S. typhimurium infection after Runx3 deletion. (A–I) Control and cKO mice were orally infected with S. typhimurium (n = 6 per group). (A,B) Colon length, (C) change of bodyweight and (D) colon histology stained with haematoxylin and eosin were measured 4 days after oral infection before sacrifice. (E–H) LPL cells isolated from infected wild type or Runx3 KO mice were stimulated and a flow cytometry assay was performed 4 h later. (E) Intracellular IFNγ and TNFα in intestinal ILC1s was are the second and fourth line, respectively, and intracellular IFNγ in intestinal NCR+ILC3s is the third line. (F) Absolute cell number of the indicated cell types from wild type or cKO mice in the intestines after infection. (G) A flow cytometry assay was performed and the intracellular IFNγ produced by intestinal ILC1s and NCR+ILC3s was measured. Isotype controls are shaded curves, control groups are blue curves and cKO groups are red curves. (H) Mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) of IFNγ in the indicated cell types. (I) Apoptosis of intestinal ILC1s and NCR+ILC3s labeled with annexin V. (mean ± SD of three samples in (B–D,F,H,I); *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001 by Student's t-test). Data are from one experiment representative of five independent experiments with similar results in (A–H).