Table 2.
One–R classifier results and confusion matrix.
| Confusion Matrix | Classifier: One-R | ||
|---|---|---|---|
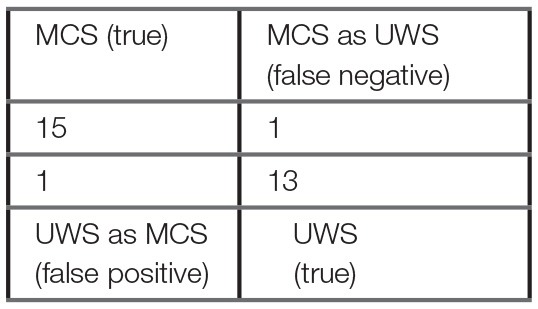 |
Rule: CIl < 4.876 → UWS CIl ≥ 4.876 → MCS |
||
| Test dataset results | |||
| Full training test (S1 group) | 10-fold cross-validation | fMRI test (S2 subgroup) | |
| True positive (MCS) rate (%) | 94 | 88 | 92 |
| True negative (UWS) rate (%) | 93 | 93 | 100 |
| False negative rate (%) | 6 | 13 | 8 |
| False positive rate (%) | 7 | 7 | 0 |
| Precision MCS classification (%) | 94 | 94 | 100 |
| Precision UWS classification (%) | 93 | 87 | 91 |
| accuracy (%) | 93 | 90 | 95 |
| F1-score (%) | 94 | 90 | 96 |
| Matthews Correlation Coefficient[−1:1] | 0.87 | 0.80 | 0.91 |
The confusion matrix is based on the S1 group. The One-R classifier is a simple machine learning decision tree model that derives a single rule from the single most contributing parameter to predict the patient's diagnosis. This model deduced that the long term complexity index (CIl) is the best predictor of patient's diagnosis, with a threshold of ~4.9, below which the patient should be diagnosed as unresponsive (UWS) and above as minimally conscious (MCS). The 10-fold cross-validation test shows that this model is quite robust and reliable, with 90% accuracy, 7% false positive rate, 13% false negative rate and a F1-score, combining both accuracy and recall, of 90%. For comparison, a baseline Zero-R rule always predicting MCS as the diagnosis would have an accuracy of 53% on the S1 group dataset. Additional machine learning models and results can be found in the Supplementary materials (Appendix A).
