FIGURE 6. PPARγ directly binds to PPREs in the MUC5AC promoter.
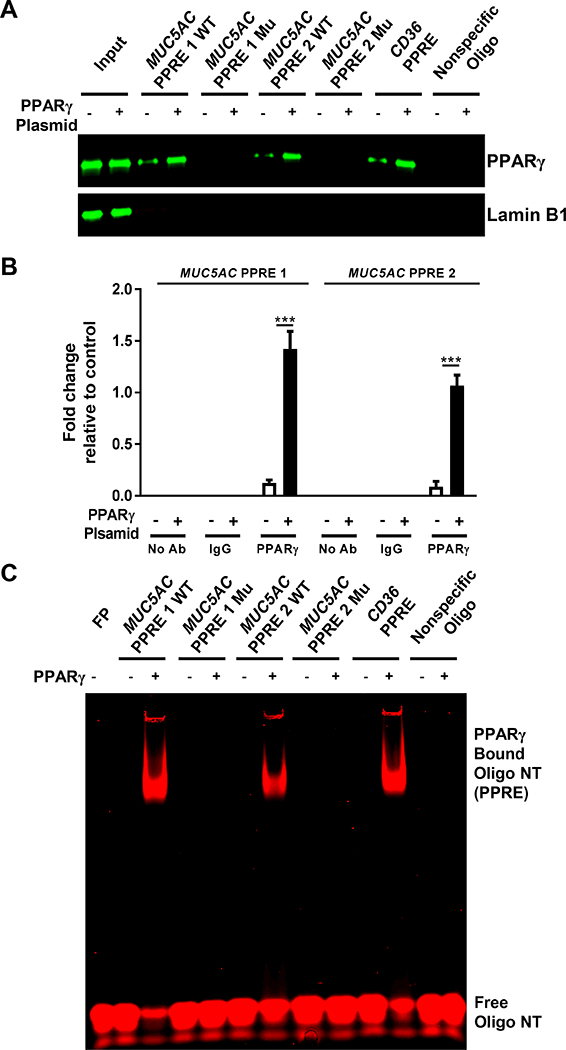
(A, B) NHBE cells were transfected with or without PPARγ expression plasmid. After 24 h, (A) nuclear extracts were obtained and incubated with the indicated biotinylated, double-stranded oligonucleotide-coupled beads. Bead-bound oligonucleotide-protein complexes were eluted and subjected to Western blotting to identify the presence of PPARγ. The PPRE from the CD36 gene and a nonspecific nucleotide sequence were used as positive and negative controls, respectively. Nuclear extracts without added nucleotides were loaded as input. Western blotting for Lamin B1 was performed as a control for non-specific interaction. (B) Chromatin was crosslinked and immunoprecipitated with antibodies against IgG or PPARγ; the antibody-bound DNA-protein complexes were then subjected to real-time RT-PCR with primers that specifically amplified the MUC5AC PPRE1 and PPRE2 regions. (C) Recombinant PPARγ was individually incubated with infrared dye 700 end-labeled double-stranded oligonucleotides for WT or mutated (Mu) MUC5AC PPRE, CD36 PPRE, or nonspecific oligonucleotide. EMSA was performed as described in Materials and Methods. The infrared signal (red) was detected using an Odyssey Infrared Imager. The data are expressed as the mean ± SD with n = 3. The results were reproduced at least two times independently; ***P < 0.001
