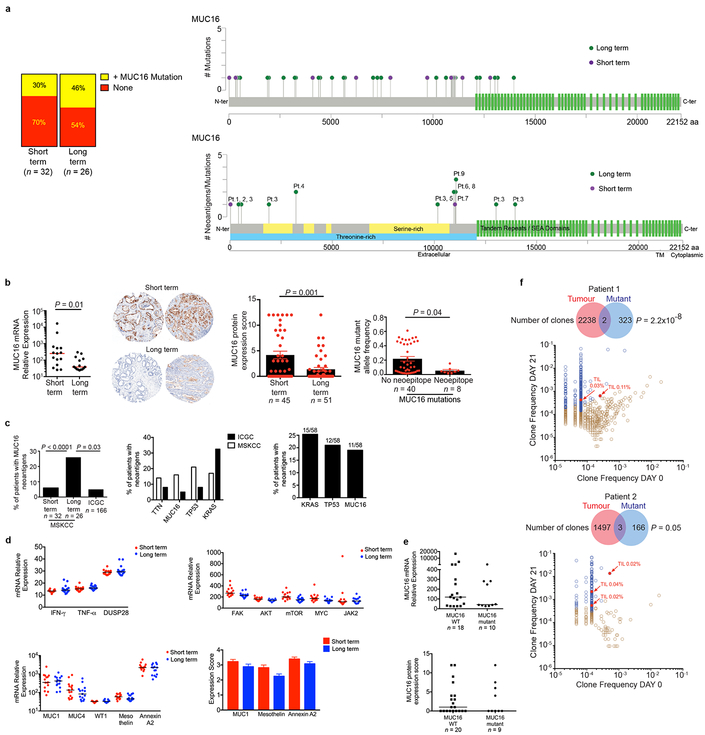
Extended Data Figure 9|. Long term survivors do not display differences in MUC16 mutations, transcriptional regulators or downstream targets of MUC16, or differences in other mucins and tissue expression antigens.
a, The frequency of MUC16 mutations in short and long term PDAC tumors. Lollipop plot showing location of MUC16 mutations and neoantigens in short and long term pancreatic cancer survivors. b, (left) Bulk tumor MUC16 mRNA, and (middle) protein expression by immunohistochemistry. Immunohistochemical staining was repeated independently in triplicates for each patient. (right) MUC16 mutant allele frequency in non-hypermutated tumors with MUC16 mutations. c, (left) Frequency of patients with MUC16 neoantigens in MSKCC and ICGC cohorts. (middle) Frequency of patients with neoantigens in genes recurrently harboring neoantigens in >5% of patients in both MSKCC and ICGC cohorts. (right) Genes most frequently harboring neoantigens in the MSKCC cohort as determined by pVACSeq. Frequency of patients (y-axis) and raw numbers (above bar graphs) are indicated. d, mRNA expression of transcriptional activators of MUC16 (top left), mediators implicated in MUC16 dependent tumor progression (top right), and mRNA (bottom left) and protein (bottom right) of tissue expression antigens MUC1, MUC4, WT1, mesothelin, and Annexin A2 in short and long term tumors. WT1 protein was undetectable in both short and long term survivors. n=15 per group in top left, top right, and bottom left; short term n=45, long term n=51 in bottom right. e, MUC16 mRNA and protein expression in MUC16 non-mutated (WT; n=18 (top), n=20 (bottom)) and mutated (mutant; n=10 (top), n=9 (bottom)) tumors. f, TCRVβ sequencing of T cell product following peripheral blood T cells pulse with MUC16 neopeptides as in Figure 4e. Brown open circles – stable/contracted clones with mutant neopeptide; blue open circles – expanded clones with mutant neopeptide; red solid circles - expanded clones with mutant neopeptide detected in archival primary tumors. Arrows = clones in archival primary tumors with rank frequencies. Venn diagrams = clonal overlap in respective compartments. Horizontal bars, median values; error bars, mean ± SEM. n = biologically independent samples in individual patients. P-values were determined using two-tailed Mann Whitney and Students t-tests (b), Chi-square tests (c), and as described in the methods (f).