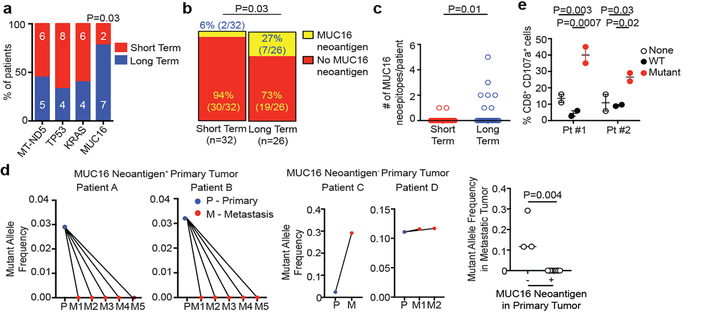
Figure 4: MUC16 is a neoantigenic hotspot in pancreatic cancer survivors.
(a) Genes with neoantigens in >15% of patients. (b) MUC16 neoantigen frequency and (c) number. Short term n=32, long term n=26 in (a), (b), and (c). (d) Metastatic propagation of all clones in the primary tumor stratified by the presence/absence of MUC16 neoantigens. Mutant allele frequencies in matched primary-metastatic tumors (left) and metastatic tumors alone (far right) are shown in biologically independent samples in four patients. (e) CD8+ T cell degranulation in PBMCs pulsed with no peptide (None), MUC16 neopeptide (Mutant), and control WT peptide (WT). Data in (e) are representative of two independent experiments with similar results. n = biologically independent samples in individual patients. Horizontal bars, median values. Error bars, mean ± SEM. P values were determined in (a, b) using two-sided Chi-square test, in (c, d) using two-tailed Mann-Whitney test, and in (e) using two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparison test.