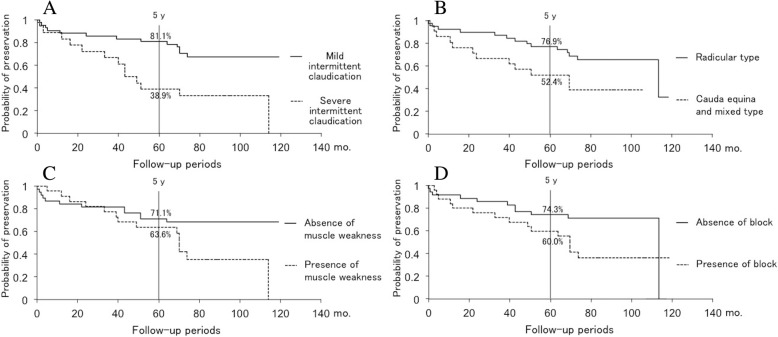
Fig. 2.
a Comparison of symptom preservation in patients with severe versus mild intermittent claudication using Kaplan-Meier analysis. The outcomes of conservative treatment were worse in patients with severe intermittent claudication at the initial visit (≤ 100 m) than those in patients with mild intermittent claudication (between 100 and 500 m) (p = 0.004). b Comparison of symptom preservation in patients with radicular versus cauda equina or mixed type using Kaplan-Meier analysis. The outcomes of conservative treatment were worse in patients with cauda equina or mixed-type LSS than those in patients with radicular-type LSS (p = 0.039). c Comparison of symptom preservation in patients with versus without lower limb weakness using Kaplan-Meier analysis. The outcomes of conservative treatment were worse in patients with lower limb muscle weakness than those in patients with no muscle weakness (p = 0.049). d Comparison of symptom preservation by absence or presence of block on myelography using Kaplan-Meier analysis. The outcomes of conservative treatment were worse in patients with block on myelography than those in patients with no block on myelography (p = 0.045)