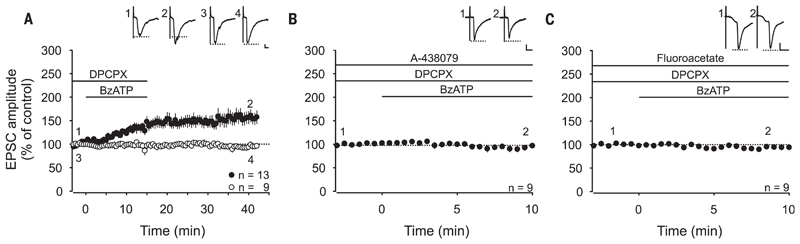
Fig. 1. Activation of spinal P2X7 receptors induces gliogenic LTP at C-fiber synapses.
Recordings were performed on lamina I neurons with independent monosynaptic C-fiber inputs from two dorsal root halves. Amplitudes of EPSCs were normalized to six baseline values, and the mean (±1 SEM) was plotted against time (min). Horizontal bars indicate drug application. (A) DPCPX (1 μM) application started at time point −3 min. Bath application of BzATP (100 μM) started at time point 0 min and induced LTP at 13 out of 22 C-fiber inputs (filled circles) (P < 0.001, at 30 min of wash-out compared with control values). At 9 out of 22 C-fiber inputs, BzATP did not influence EPSC amplitudes (open circles) (P = 0.650, at 30 min of wash-out compared with control values). (B) Bath application of the P2X7R antagonist A-438079 (10 μM) 13 min before BzATP prevented the BzATP-induced LTP at all C-fiber inputs tested (n = 9, P = 0.054, at 10 min compared with baseline). (C) In the presence of fluoroacetate (10 μM), BzATP had no effect on synaptic transmission (n = 9, P = 0.114 at 10 min compared to baseline). Insets show individual EPSCs at indicated time points. Calibration bars indicate 50 pA and 10 ms. Statistical significance was determined by using repeated measures analysis of variance (RM ANOVA) followed by Bonferroni t test. Paired t test was used for control recordings.