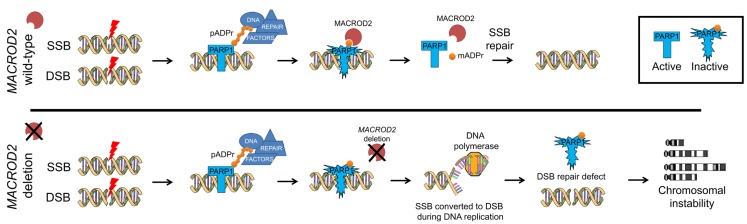
Figure 1. Focal deletion of MACROD2 results in deficient MACROD2 mono-ADP-ribosylhydrolase activity.
As a consequence, removal of the terminal autoinhibitory mono-ADP-ribose moiety from PARP1 is compromised, resulting in impaired PARP1 transferase activity, associated with defective DNA repair and increased sensitivity to DNA damage. DNA repair deficiency, accompanied by chromosome segregation errors and centrosome amplification, cumulates in CIN contributing to intra-tumor genetic heterogeneity and cancer progression.