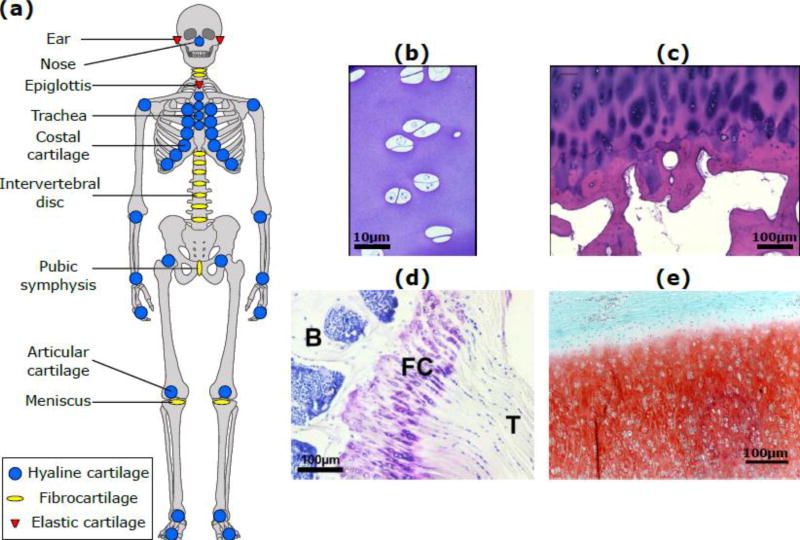
Figure 1. Anatomical locations and microscopic structure of cartilage.
(a) Locations of hyaline cartilage (blue), fibrocartilage (yellow) and elastic cartilage (red) in the human body; (b) Immature bovine articular cartilage; (c) Human adult articular cartilage (83 year old male donor distal femur) showing chondrocyte clustering near the tidemark, typical of osteoarthritis; (d) Murine fibrous cartilage (FC) at the interface of the supraspinatus tendon (T) and the humeral head of the humerus bone (B); (e) Elastic cartilage of neonatal bovine ear; elastin fibers appear as unstained lines between the safranin-O staining for GAGs