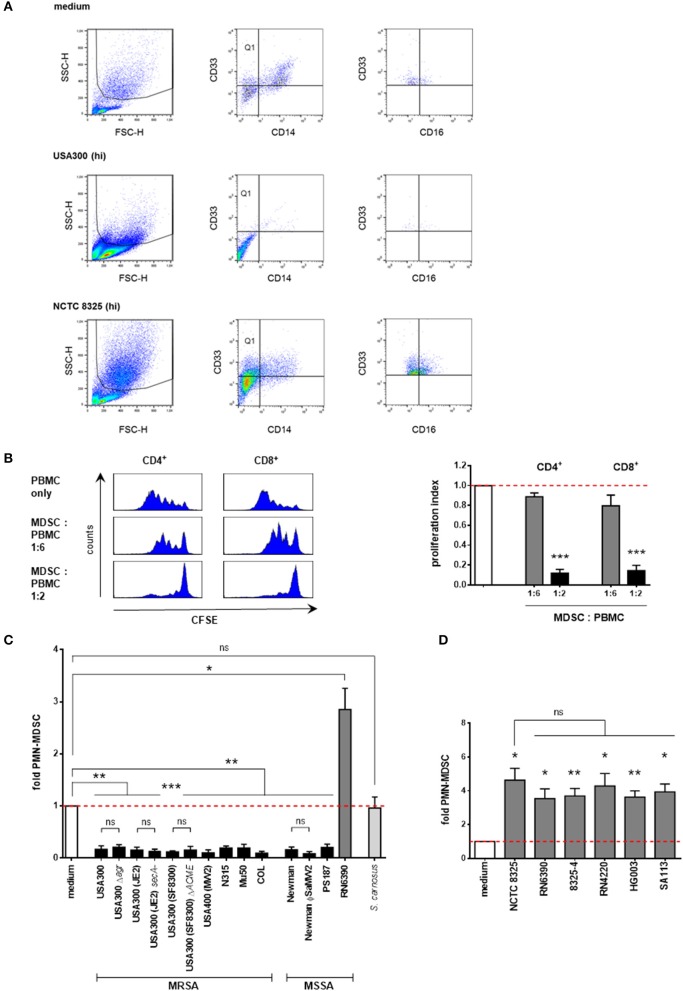
Figure 1.
Supernatants from S. aureus strains differentially modulate PMN-like MDSC levels. PBMC were stimulated with supernatants prepared from overnight cultures of the indicated staphylococcal strains and PMN-like MDSC were assessed by flow cytometry. (A) Phenotypic determination of PMN-like MDSC in PBMC. The granulocytic region was gated in the forward-side-scatter. Afterwards CD33+CD14− cells (Quadrant Q1) were gated and PMN-like MDSC were determined as SSChighCD33+CD14− cells. Further flowcytrometric analysis revealed that these granulocytic cells are partly CD16+. The dot plots illustrate the modulation of PMN-like MDSC mediated by supernatants from NCTC 8325 and USA300 [at 3% (hi) concentration] as compared to medium only. (B) S. aureus-induced PMN-MDSC dose-dependently suppress T-cell proliferation. PMN-like MDSC were induced using 0.02% of USA300 supernatants, isolated by CD33 MACS separation and co-cultured for 4 days with freshly isolated, CFSE-stained PBMC at given ratios. CFSE-fluorescence intensity of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells was analyzed by flow cytometry. Left panel: Histograms showing suppression of T cell proliferation. Right panel: Bars represent the proliferation index. The values are normalized to the proliferation of CD4+ cells or CD8+ T cells without addition of MDSC. Bars represent means ± SEM. Differences between MDSC co-cultures and controls were analyzed by a one-sample t-test. (C) Screening of S. aureus supernatants for modulation of PMN-like MDSC induction. PBMC were stimulated using 3 vol.% of supernatants prepared from overnight cultures of the indicated staphylococcal strains. Except for RN6390, all tested S. aureus strains inhibited the PMN-like MDSC formation. S. aureus strains are illustrated in black bars except for NCTC 8325 members (shown in dark gray bars). S. carnosus is shown in light gray bars. (D) Screening of NCTC 8325 derivative strains. All tested members of the NCTC 8325 family consistently induced PMN-like MDSC. Bars represent means ± SEM. Differences between stimulations and controls (C,D) were analyzed by a one-sample t-test. Differences between different wild-type and mutant S. aureus strains (C,D) were analyzed by a Mann-Whitney test or by an unpaired t-test. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; ns–not significant.