Figure 6 – Upregulation of ARID1B restores RNAPII pausing and transcription at most genes.
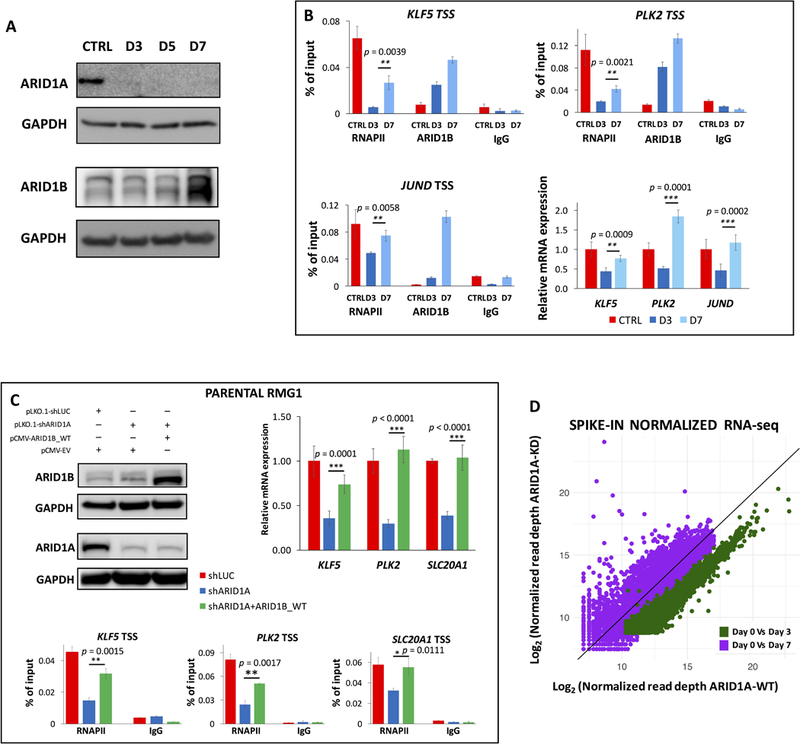
(A) Immunoblot analysis of ARID1A and ARID1B during a time course of doxycycline (days 3, 5, 7). ARID1B is increasingly upregulated in response to ARID1A depletion, peaking at day 7. Quantitative immunoblots are shown in Supplemental Fig. S4H. (B) ChIP-qPCR analysis of RNAPII and ARID1B binding for a panel of ARID1A target genes at 0 hours (CTRL), 3 days, and 7 days of treatment with doxycycline. ARID1B gradually replaces ARID1A at the TSS, whilst RNAPII proximal-promoter occupancy is restored. Similarly, qRT-PCR for the same genes (fold enrichment compared to CTRL, normalized to 18S rRNA) suggests that transcription resumes its physiological level at day 7, concurrent with highest occupancy of ARID1B. (C) Parental RMG-1 cells were transduced with shRNAs against ARID1A and a full-length ARID1B vector. ChIP-qPCR for RNAPII, and qRT-PCR at three candidate loci, show that ARID1A-dependent transcriptional regulation is complemented (p<0.0111) by ARID1B (qRT-PCR fold change compared to shLUC, normalized by 18s rRNA). (D) Correlation plot (spike-in normalized RNA-seq) for all expressed coding genes shows that global transcriptional downregulation provoked by ARID1A depletion (day 3 of DOX induction, green) is largely rescued by ARID1B upregulation (day 7 of DOX induction, purple). Genes that are persistently dysregulated at day 7 have been functionally evaluated (IPA) and may represent ARID1A-specific targets.
