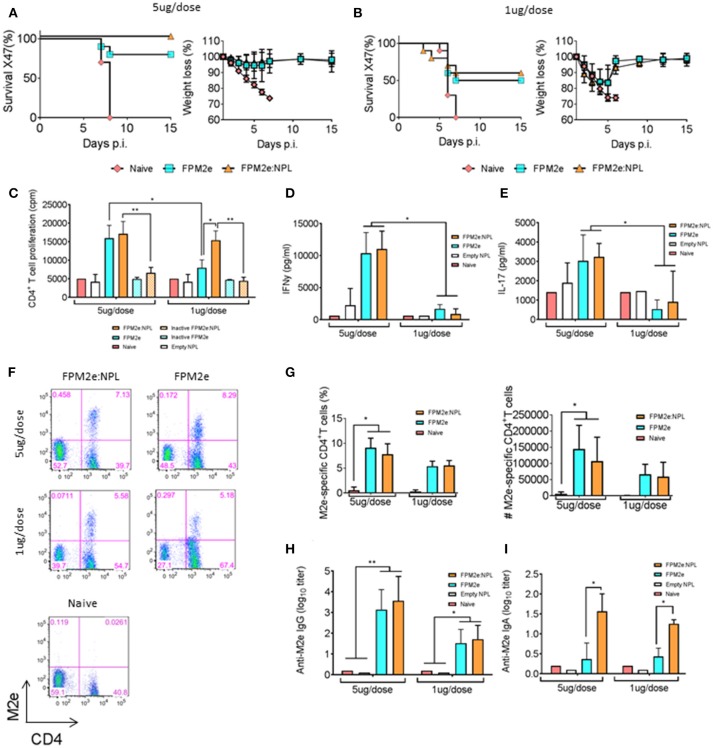
Figure 2.
Enhanced immunogenicity of the combined NPL vaccine vector. (A,B) Survival and weight loss were monitored in influenza virus challenged Balb/c mice following three i.n immunizations with 5 μg (A) or 1 μg (B) of FPM2e or FPM2e:NPL. The percent of surviving mice (left panel) and body weight loss (right panel) following a challenge infection with 4 × LD50 of the mouse adapted X47 virus strain are plotted. (C) Recall responses to M2e-peptide in primed CD4+ T cells following i.n immunizations with 5 or 1 μg of enzymatically active or inactive mutant FPM2e or FPM2e:NPL or empty NPL w/o FPM2e, as indicated. Mean proliferation in isolated splenocytes to M2e peptide is given as mean c.p.m ± S.E.M. (D,E) The production of IFN-γ (D) or IL-17A (E) to recall stimulation with M2e-peptide of the primed CD4+ T cells (as in C) is given in pg/ml ± SD. (F,G) Representative FACS plots of M2e-tetramer+ CD4+ T cells in the lungs of i.n immunized and challenged mice as indicated (F). The percentage (left panel) and absolute number (right panel) of antigen primed M2e+ tetramer CD4+ T cells (G). (H,I) M2e specific IgG antibodies in serum (H) or IgA antibodies in BAL (I) were measured by ELISA in Balb/c mice immunized i.n. with FPM2e, FPM2e:NPL or PBS (naïve), as indicated, and given as mean log10-titers ± SD of 3 independent experiments giving similar results. Statistical significance was calculated by unpaired t-test and p-values are given as *p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01.