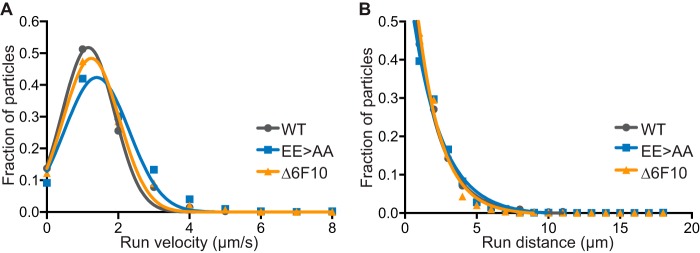
FIG 3.
Mutation of the VP5 upper domain did not impair retrograde axonal transport. Primary sensory neurons were infected with derivatives of the VP5 wild type (WT), glutamic acid mutant (EE>AA), and Δ6F10 mutant that encode an mCherry-VP24 fusion to allow for tracking of individual capsids in axons. Intracellular capsid transport was monitored by time-lapse fluorescence microscopy during the first hour of infection. Run velocity (A) and run distance (B) profiles of individual capsids are representative of three independent experiments.