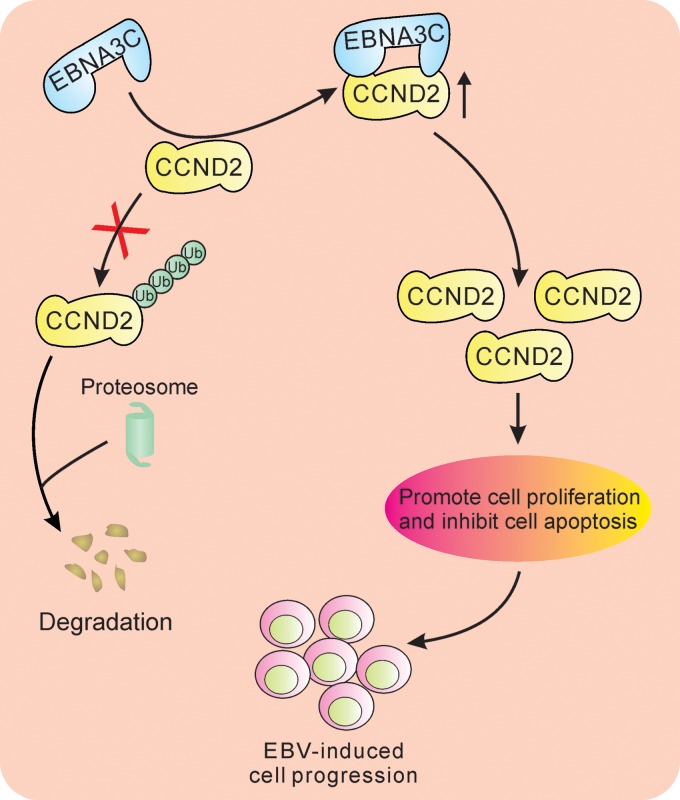
FIG 7.
Schematic model showing the modulation of the cyclin D2 function by EBNA3C. EBNA3C associates with cyclin D2 and enhances its stability at the protein level through inhibition of its ubiquitin-mediated degradation. The EBNA3C-cyclin D2 interaction ultimately drives cell proliferation, which leads to lymphomagenesis.