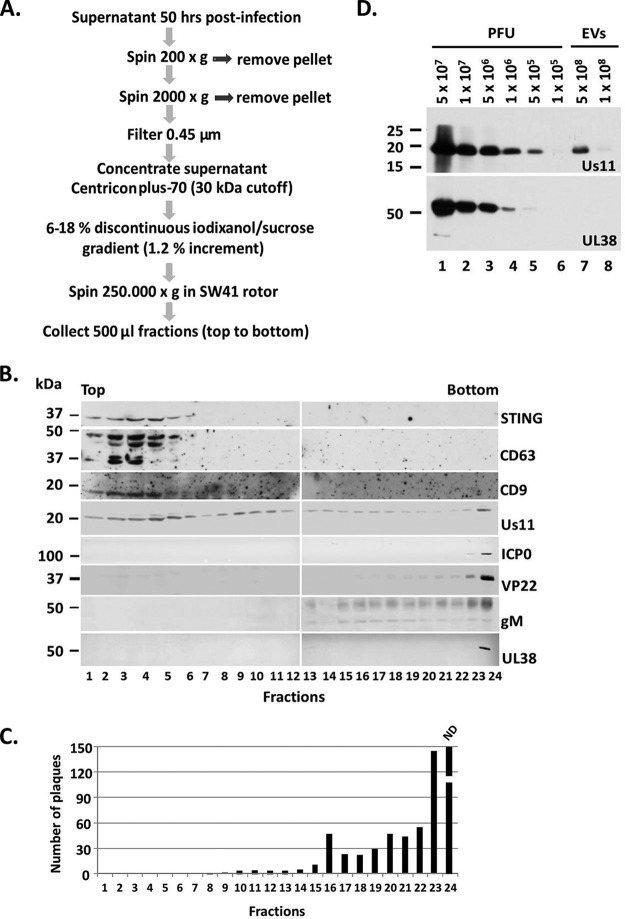
FIG 1.
Separation of EVs from HSV virions. (A) Procedures to separate EVs from HSV-1 virions. (B) The proteins present in the fractions collected from procedures in panel A were separated in denaturing polyacrylamide gels, transferred to nitrocellulose sheets, and immunoblotted with the mouse monoclonal antibodies to STING, Us11, and the rabbit polyclonal antibodies for CD63, CD9, ICP0, VP22, gM, and UL38. (C) The fractions presented in panel B were incubated with Vero cells in a virus plaque assay. The cells exposed to the bottom fraction of the gradient (fraction number 24) were fully infected so plaques could not be determined. ND, not determined. (D) Assessment of the detection limit of the Us11 and UL38 antibodies by immunoblot analysis using different amounts of HSV-1 infectious particles. The viral protein Us11, but not UL38, was found in the EV fractions derived from infected cells.