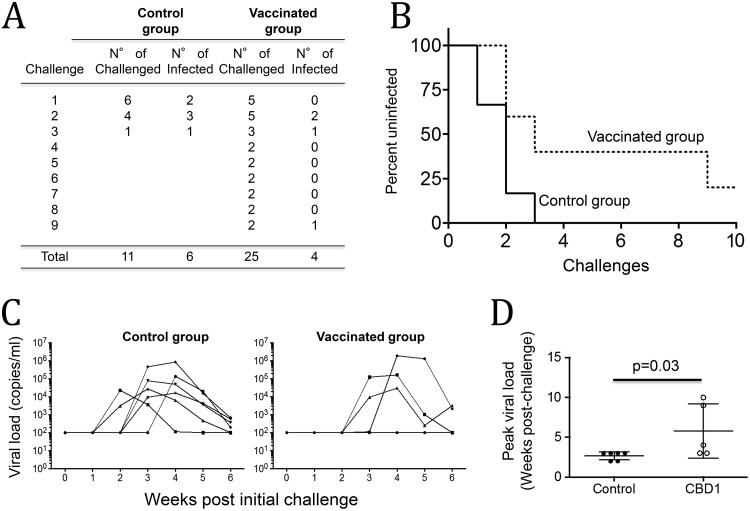
FIG 3.
Protective effect of CBD1/CBM vaccination. Six months after the fourth vaccine boost, animals were challenged with a repetitive low dose of SHIV162P3 (0.33 AID50; NIH) via the mucosal rectal route. (A) Acquisition rates in both control and CBD1/CBM-vaccinated monkeys. All animals from the control group were infected after 1 to 3 challenges with SHIV162P3. The difference between vaccinated and control groups was evaluated using Fisher's exact test (P = 0.03). (B) Survival curves of CBD1/CBM-vaccinated macaques versus controls. Statistical significance was evaluated using the Mantel-Cox test (P = 0.05). (C) Plasma viral loads of SHIV162P3-infected monkeys were evaluated by quantitative RT-PCR. (D) Peak viral load in control (closed symbols) and CBD1/CBM-vaccinated (open symbols) macaques. We arbitrarily considered the peak of viral load for the uninfected monkey at week 10. Statistical significance was evaluated using the Mann-Whitney test.