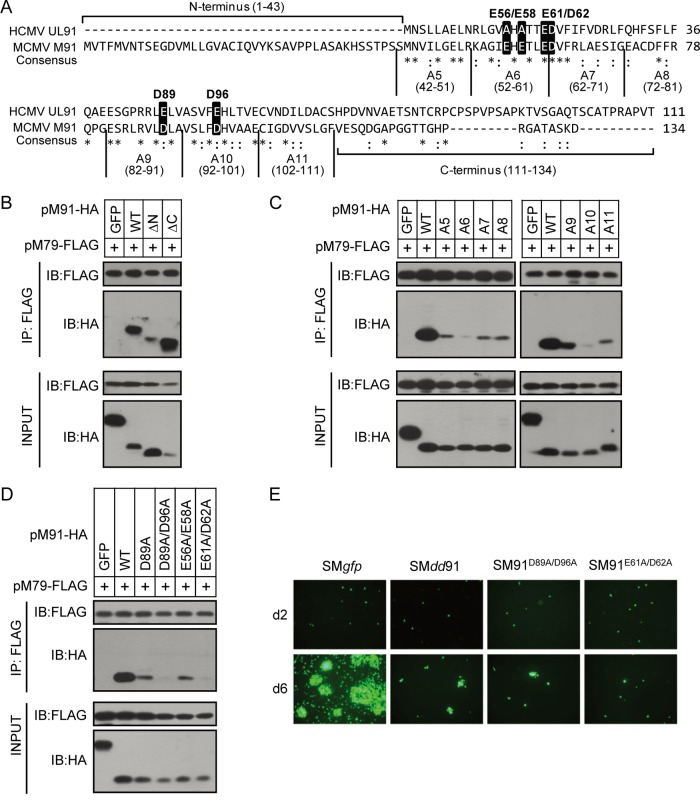
FIG 6.
Identification of the functional regions of pM91 for its interaction with pM79. (A) Protein sequence alignment of pM91 (MCMV) and the HCMV homolog pUL91. Identical and conserved amino acids are represented by asterisks and colons, respectively. The alanine scanning mutants used in panel C are also labeled. The amino acids in the black boxes indicate the positions mutated in panel D. (B, C, D) HEK293T cells were cotransfected with FLAG-tagged pM79 and either HA-tagged GFP (negative control), pM91 (wild type [WT]), or mutant pM91. Cell lysates were used for immunoprecipitation (IP) with anti-FLAG M2 beads, followed by immunoblotting (IB) with the indicated antibodies. pM91 truncated mutations included the N-terminus deletion (ΔN) and the C-terminus deletion (ΔC). A5 to A11 are pM91 alanine scanning mutants. D89A, D89A/D96A, E56A/E58A, and E61A/D62A indicate pM91 point mutants. (E) MEF10.1 cells were transfected with wild-type BAC pSMgfp or pSMdd91, pSM91D89A/D96A, and pSM91E61A/D62A mutant BACs, and the GFP signals were observed using fluorescence microscopy.