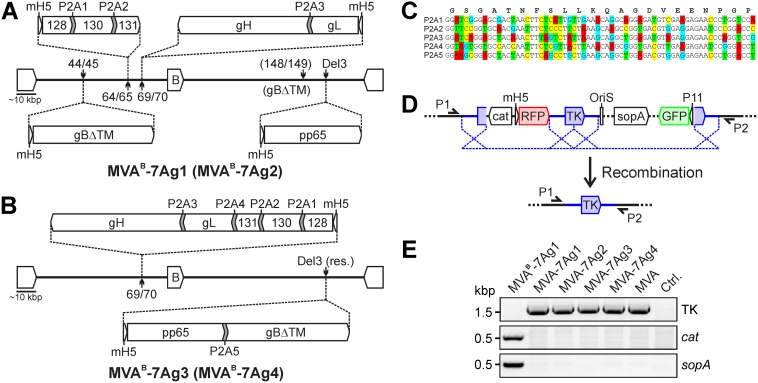
FIG 1.
Construction of MVA expressing multiple HCMV antigens. (A and B) Vector construction. Utilizing MVABAC-TK, P2A-linked polycistronic and single antigen expression constructs of the PC subunits (gH, gL, UL128, UL130, and UL131A), gB (without TM), and pp65 were inserted as indicated into different intergenic regions (44/45, 64/45, 69/70, and 148/149), the deletion 3 site (Del3), or a restructured Del3 site (Del3 res.) to generate MVAB-7Ag1, MVAB-7Ag2, MVAB-7Ag3, and MVAB-7Ag4. Different P2A codon sequences (P2A1 to P2A5) were used to link the antigens. mH5, modified H5 promoter; B, BAC vector. (C) P2A codon sequences. The lower 5 lines indicate the different P2A codon sequences with mutated nucleotides (marked in colors) that were used for the vector construction as shown in panels A and B. The upper line shows the amino acid sequence of the P2A peptide. (D and E) BAC removal. A genomic duplication (blue in panel D) was utilized to seamlessly remove the BAC sequences (cat, OriS, sopA, RFP, and GFP) of the different MVA vectors by homologous recombination, resulting in MVA-7Ag1, MVA-7Ag2, MVA-7Ag3, and MVA-7Ag4. TK, thymidine kinase gene; P11, vaccinia virus P11 promoter. Primers P1 and P2 flanking the TK gene and primers specific for cat and sopA were used to confirm the restoration of the TK gene and absence of residual BAC sequences via PCR in DNA isolated from BHK cells infected with rMVA. BHK cells infected with MVAB-7Ag1 containing the BAC vector or parental MVA as well as uninfected cells were analyzed for controls.