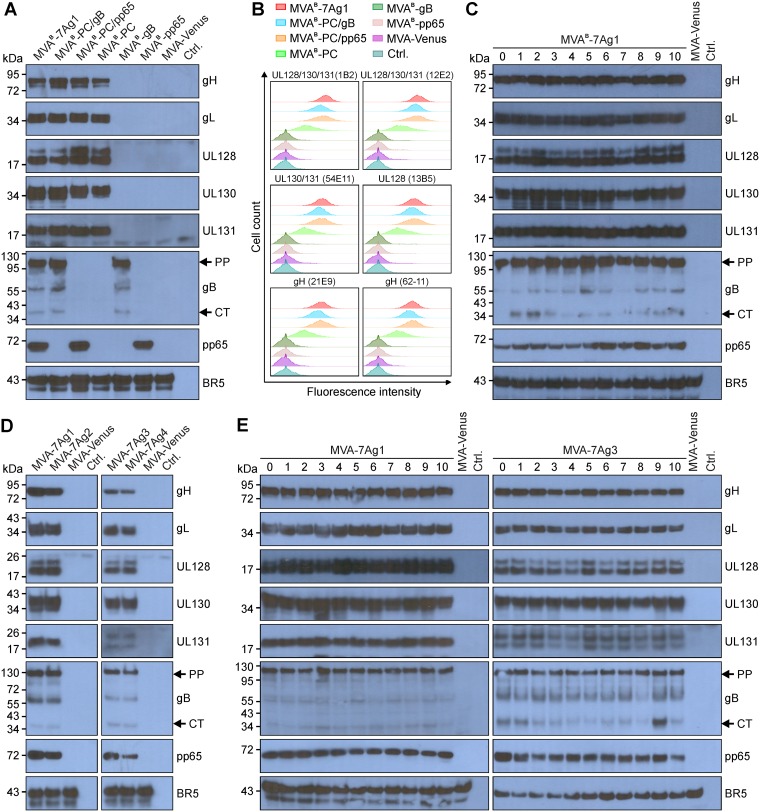
FIG 2.
HCMV antigen expression by multiantigenic MVA vectors. (A and B) Immunoblot (A) and flow cytometry (B) analyses were used to compare the HCMV antigen expression by MVAB-7Ag1 and the control vectors (MVAB-PC/gB, MVAB-PC/pp65, MVAB-PC, MVAB-gB, and MVAB-pp65). Monoclonal (gH, UL130, gB, and pp65) and polyclonal (gL, UL128, and UL131A) antibody preparations were used to detect the HCMV antigens in whole-cell lysates of MVA-infected CEF via immunblotting (A). NAb specific for epitopes formed by UL128/130/131A (1B2 and 12E2), UL130/131A (54E11), UL128 (13B5), or gH (21E9 and 62-11) were used to detect cell surface expression of the PC subunits on live, nonpermeabilized BHK cells infected with rMVA (B). (C to E) Immunoblot analysis as described for panel A was used to evaluate the HCMV antigen expression by MVAB-7Ag1 following 10 (lanes 0 to 10) virus passages in CEF (C), by MVA-7Ag1, MVA-7Ag2, MVA-7Ag3, and MVA-7Ag4 following BAC vector removal (D), and by MVA-7Ag1 and MVA-7Ag3 following 10 virus passages in CEF (E). Vaccinia virus BR5 was detected in panels A and C to E for loading control. Arrows in panels A and C to E indicate the precursor protein (PP) and C-terminal cleavage product (CT) of gB. CEF infected with MVA expressing the fluorescence marker Venus (MVA-Venus) or uninfected cells (Ctrl.) were analyzed as additional controls for panels A and C to E. The x axis in B represents the log10 of fluorescence intensity, and the y axis represents cell count.