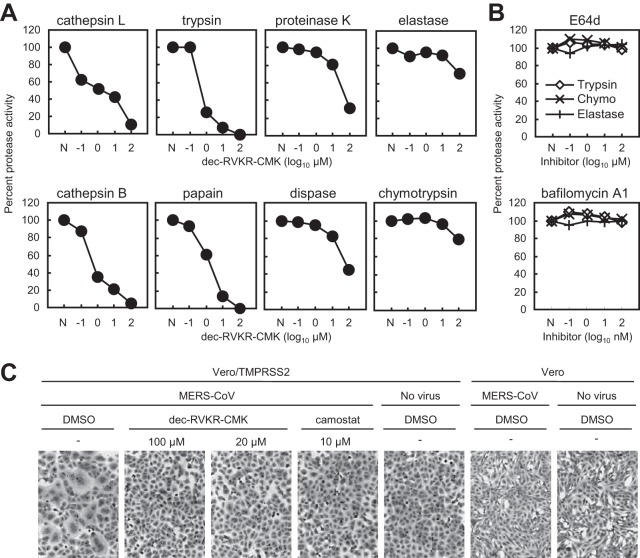
FIG 8.
Effect of furin inhibitor on commercial proteases and cell surface TMPRSS2. (A) Inhibitory effect of dec-RVKR-CMK on commercial proteases. Degradation products of fluorescein-labeled casein generated by treatment with commercial proteases, cathepsin L (20 μg/ml), cathepsin B (20 μg/ml), trypsin (50 μg/ml), papain (0.3 units/ml), proteinase K (0.3 units/ml), dispase (3 units/ml), elastase (200 μg/ml), and chymotrypsin (10 μg/ml), at 37°C for 30 min in the presence of dec-RVKR-CMK (serially diluted 10-fold) were quantified by fluorometry (n = 3). Data are expressed as average percentages relative to that in the absence of dec-RVKR-CMK. N, no inhibitor treatment. (B) E64d and bafilomycin A1 do not inhibit commercial proteases. E64d or bafilomycin A1 was used instead of dec-RVKR-CMK; all experiments were carried out as described for panel A (proteases tested were trypsin, chymotrypsin, and elastase). (C) Inhibitory effect of dec-RVKR-CMK against TMPRSS2, as assessed in the FFWO assay. A high titer of MERS-CoV (MOI = 10) was adsorbed onto Vero/TMPRSS2 or Vero cells (on ice for 1 h). Cells were then incubated at 37°C in the presence of the inhibitor. After 5 h, cells were fixed and stained with crystal violet. DMSO, dimethyl sulfoxide.