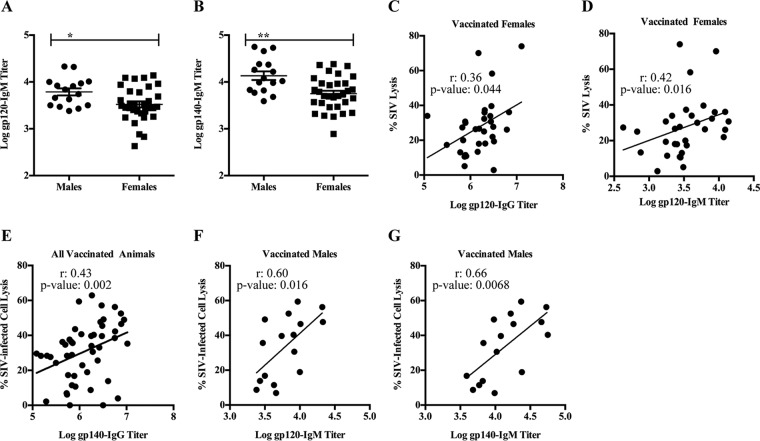
FIG 4.
Env-specific IgG/IgM exhibit different ADCML capabilities in males and females. (A and B) Env-specific IgM binding titers were assessed in sera collected from all vaccinated macaques. gp120-specific (A) and gp140-specific (B) IgM binding titers are shown; error bars indicate SEM, and asterisks indicate significant differences between males and females (*, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01). (C and D) Statistical correlations between ADCML of SIV and gp120-specific IgG binding titers (C) and IgM binding titers (D) are shown for all vaccinated females. (E to G) Statistical correlations between ADCML of SIV-infected H9 cells and gp140-specific IgG binding titers in all vaccinated animals (E) and gp120-specific (F) and gp140-specific (G) IgM binding titers in all vaccinated males are shown. The animal cohorts are displayed within each graph heading, and the symbols represent values from individual macaques. Significant correlations, calculated using Spearman's rank correlation coefficient, are indicated by r and P values and linear regression trend lines (added for visual aid).