Figure 2.
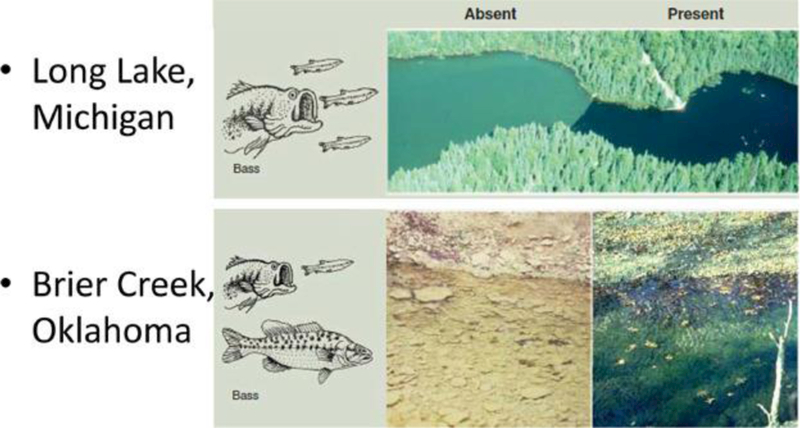
Top: Long Lake (Michigan) with largemouth bass experimentally removed (left) and present (right). Bass indirectly reduce phytoplankton (thereby increasing water clarity) by limiting smaller zooplanktivorous fish, thus causing zooplankton to increase and phytoplankton to decline 94. Bottom: Pools in Brier Creek, a prairie margin stream in south-central Oklahoma with (right) and lacking (left) largemouth and spotted bass. The predatory bass extirpate herbivorous minnows, promoting the growth of benthic algae 95. Adapted from Estes et al. 96.
