Figure 5.
Expression Pattern of GAP-43, pS96, and pJNK in Developing Mouse Brain
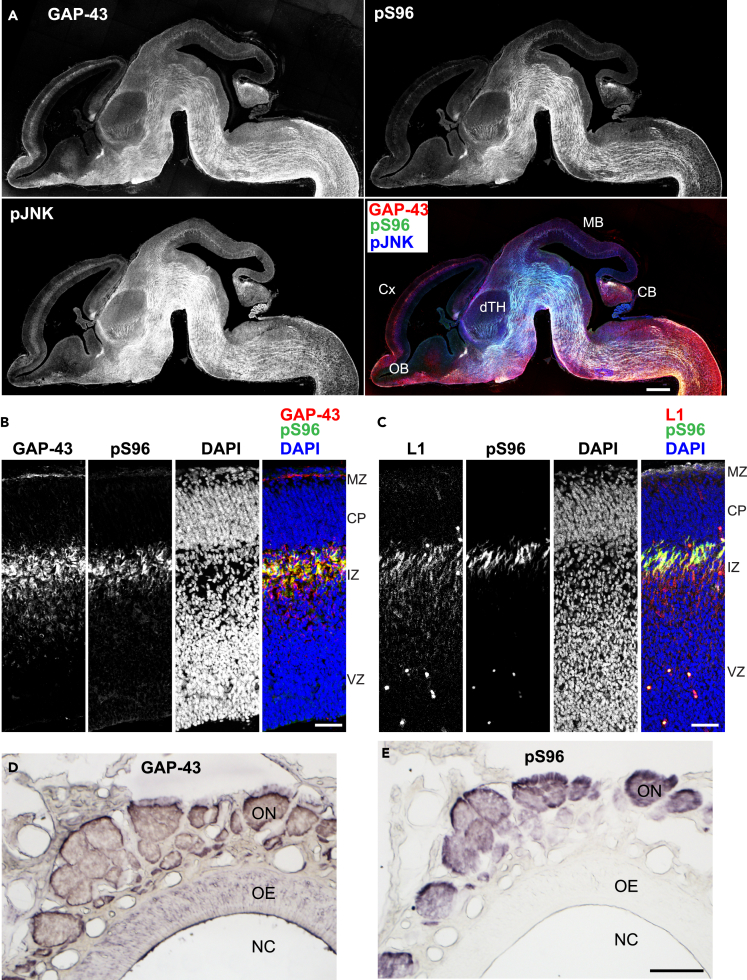
(A) Expression in an E15 parasagittal section stained with pan-GAP-43, pS96, and pJNK Abs. GAP-43 itself was expressed in most of the differentiated neurons; by contrast, pS96 was localized to axonal processes but was not detected in cell bodies. pJNK exhibited a broader distribution than GAP-43. OB, olfactory bulb; Cx, neocortex; dTH, dorsal thalamus; MB, midbrain; CB, cerebellum.
(B and C) Expression pattern of pS96 and GAP-43 (B) or pS96 and the cell adhesion molecule L1 (C). Nuclear staining with DAPI is also shown. GAP-43 itself was expressed by migrating neurons and ingrowing axons in the intermediate zone (IZ). pS96 expression was restricted to the L1-positive thalamocortical axons in the upper IZ. MZ, marginal zone; CP, cortical plate; VZ, ventricular zone.
(D and E) Expression in the primary olfactory system on P14. GAP-43 itself was expressed in the cells of the olfactory epithelium (OE) and the olfactory nerves (ON; D), whereas pS96 was localized only in the ON (E). NC, nasal cavity.
Scale bars: 50 μm.