Figure 2.
p53 Modulates p300 Autoacetylation and Acetyltransferase Activity in Cells
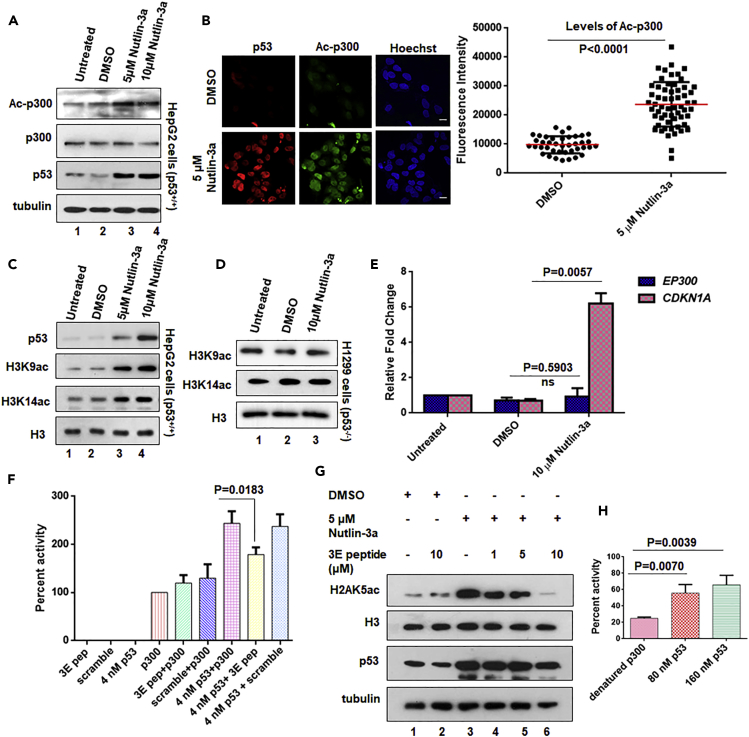
(A) HepG2 cells were treated with DMSO (vehicle control) or Nutlin-3a as indicated (lane 2–4); levels of Ac-p300, p300, and p53 were analyzed by immunoblotting. Alpha-tubulin levels were considered as the loading control.
(B) HepG2 cells were treated with 5 μM Nutlin-3a for 24 hr, and the levels of Ac-p300 and p53 were assessed by co-immunofluorescence. Fluorescence intensity of Ac-p300 in control cells versus Nutlin-3a-treated cells have been quantified (represented as mean ± SD, unpaired two-tailed Student's t test, n = 50 of three independent experiments). Scale bar, 10 μm.
(C and D) HepG2 cells (C) and H1299 cells (D) were treated with DMSO (vehicle control) or Nutlin-3a as indicated. Histone acetylation levels were analyzed by immunoblotting using H3K9ac and H3K14ac antibodies. Total histone H3 levels were used as the loading control.
(E) The relative transcript levels of EP300 and CDKN1A (p53-responsive gene) were determined by qRT-PCR (mean ± SD). Unpaired two-tailed Student's t test statistical analysis was performed. Actin transcript level was used as the internal control. The relative p300 transcripts do not alter significantly on Nutlin-3a treatment.
(F) Results of filter-binding assay indicate that the p53 phosphomimic N-terminal peptide (3E pep) can effectively reduce the activity of p300 by interfering with its interaction to p53; 4 nM p53 phosphomimic and scrambled peptides were used. (Also see Figure S1B.)
(G) HepG2 cells treated with Nutlin-3a or DMSO, and p53 phosphomimic peptide (3E peptide) as indicated, and the levels of H2AK5ac, H3, p53, and tubulin were probed by immunoblotting. (Also see Figure S1C.)
(H) The rescue of heat-denatured 20 nM p300 activity (activity rescue assay), on addition of wild-type p53, at the indicated concentrations, was determined by the in vitro filter-binding assay, using recombinant histone H3 and [3H] acetyl-CoA.