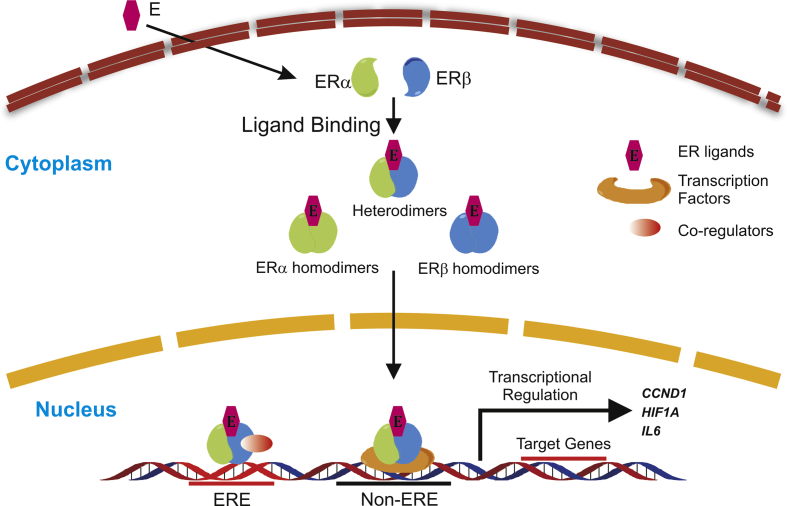
Figure 3.
ER signaling pathway. Breast cancer cells have relatively high ERα expression and low ERβ expression. These two types of nuclear hormone receptors form homo- or heterodimers upon ligand binding and translocate into the cell nucleus for transcriptional regulation, which is the main function of ERs. ER dimers bind to the ERE region of target genes and recruit co-regulators to achieve the regulation of transcriptional activity. Another mechanism by which ERs control the expression of target genes is acting as a co-regulator for other transcription factors.