Figure 1.
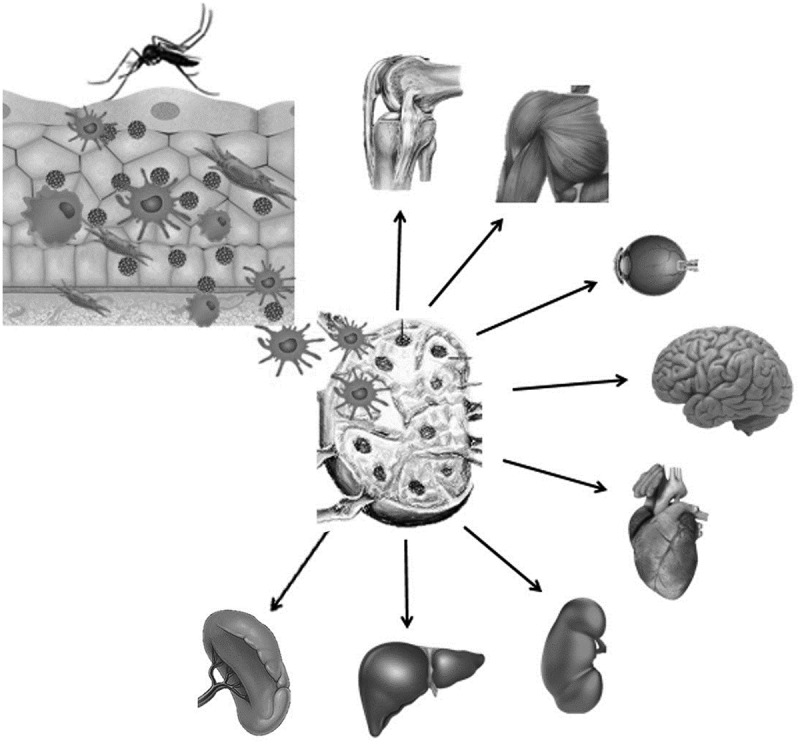
Schematic representation of the pathogenesis of chikungunya virus infection in the human host.
Notes: The virus is introduced into the skin by the bite of the infected mosquito, where it initiates replication in macrophages and cutaneous fibroblasts. Viral particles are captured by dendritic cells from the skin that carry them to the nearest lymph nodes where they will infect macrophages and monocytes. Infected monocytes enter the bloodstream carrying the viruses to multiple organs such as: liver, kidneys, heart, brain, eyes, skeletal muscles, and joints, where they replicate and induce inflammatory response.
