Figure 1. Diagram of the phosphoinositide 3-kinase pathway in oocyte physiology.
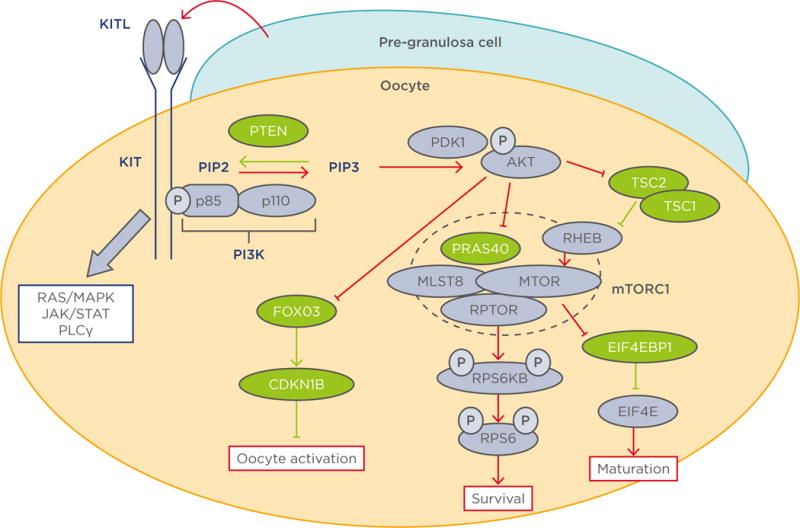
Molecules coloured green and purple are negative and positive regulators of the PI3K/AKT/mTORC1 pathway respectively. Red and green lines indicate activation and inhibition of the PI3K/AKT/mTORC1 pathway respectively.15–18·23–27,32–34,37
AKT: protein kinase B; CDKN1B: cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1B; EIF4E: eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E; EIF4EB1: eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E binding protein 1; FOXO3: forkhead box 03; JAK: janus kinase; KITL1: KIT ligand 1; MAPK: mitogen-activated protein kinase; MLST8: mTOR associated protein, LST8 homologue; mTOR: mechanistic target of rapamycin; mTORC1: mechanistic target of rapamycin; p: phosphate group; PDK1: phosphoinositide-dependent kinase-1; PI3K: phosphoinositide 3-kinase; PLCγ: phospholipase C, gamma; PTEN: phosphatase and tensin homologue; PRAS40: proline-rich AKT1 substrate of 40 kDa; RHEB: Ras homologue enriched in brain; RPS6: ribosomal protein S6; RPS6KB: ribosomal protein S6 kinase B1; RPTOR: regulatory-associated protein of mTOR; STAT: signal transducer and activator of transcription; TSC: tuberous sclerosis.
