Table 1.
Definition and Calculation of Total (whole-molecule) and Local (Atom) Linear Indices of the Molecular Pseudograph’s Atom Adjacency Matrix of the 2-Aminobenzaldehyde Molecule.
 2-Amino-benzaldehyde MolecularStructure |
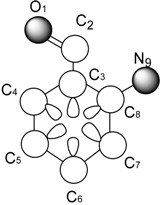 Molecular Pseudograph (G) (hydrogen suppressed-pseudograph) |
X = [O1, C2, C3, C4, C5, C6, C7, C8, N9] Molecular Vector: X∈ℜ9 In the definition of the X, as molecular vector, the chemical symbol of the element is used to indicate the corresponding electronegativity value. That is: if we write O it means χ(O), oxygen Mulliken electronegativity or some atomic property, which characterizes each atom in the molecule. Therefore, if we use the canonical basis of 9, the coordinates of any vector X coincide with the components of that molecular vector [X] = [3.17, 2.63, 2.63, 2.63, 2.63, 2.63, 2.63, 2.63, 2.33] [X]: column vector of coordinates of X in the Canonical base of R9 (a nx1 matrix) |
||||||
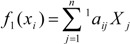 |
 |
|||||||
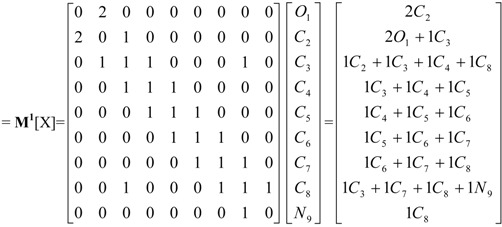
| Atom linear indices of first order is a linear map; f1(xi): ℜn→ ℜn
such that, f1(O1, C2, C3, C4, C5, C6, C7, C8, N9) = (2C2, 2O1+1C3, 1C2 +1C3+1C4+1C8, 1C3+1C4+1C5, 1C4+1C5+1C6, 1C5+1C6+1C7, 1C6+1C7+1C8, 1C3+1C7+1C8+1N9, 1C8) = (5.26, 8.97, 10.52, 7.89, 7.89, 7.89, 7.89, 10.22, 2.63) and whole-molecule linear indices of first order is a linear functional; 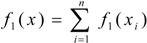 =f1(O1) + f1(C2) + f1(C3) + f1(C4) + f1(C5) + f1(C6) + f1(C7) + f1(C8) + f1(N9)= 69.16 =f1(O1) + f1(C2) + f1(C3) + f1(C4) + f1(C5) + f1(C6) + f1(C7) + f1(C8) + f1(N9)= 69.16 | ||||||||
| Local and total linear indices of order 0-5 (k = 0-5) | ||||||||
| Atom (i) | f0(xi) | f1(xi) | f2(xi) | f3(xi) | f4(xi) | f5(xi) | ||
| O1 | 3.17 | 5.26 | 17.94 | 42.08 | 146.96 | 400.72 | ||
| C2 | 2.63 | 8.97 | 21.04 | 73.48 | 200.36 | 676.25 | ||
| C3 | 2.63 | 10.52 | 37.6 | 116.2 | 382.33 | 1193.57 | ||
| C4 | 2.63 | 7.89 | 26.3 | 87.57 | 277.41 | 894.29 | ||
| C5 | 2.63 | 7.89 | 23.67 | 73.64 | 234.55 | 739.87 | ||
| C6 | 2.63 | 7.89 | 23.67 | 73.34 | 227.91 | 721.81 | ||
| C7 | 2.63 | 7.89 | 26 | 80.93 | 259.35 | 820.73 | ||
| C8 | 2.63 | 10.22 | 31.26 | 105.08 | 333.47 | 1080.23 | ||
| N9 | 2.33 | 2.63 | 10.22 | 31.26 | 105.08 | 333.47 | ||
| Total | 23.91 | 69.16 | 217.7 | 683.58 | 2167.42 | 6860.94 | ||
