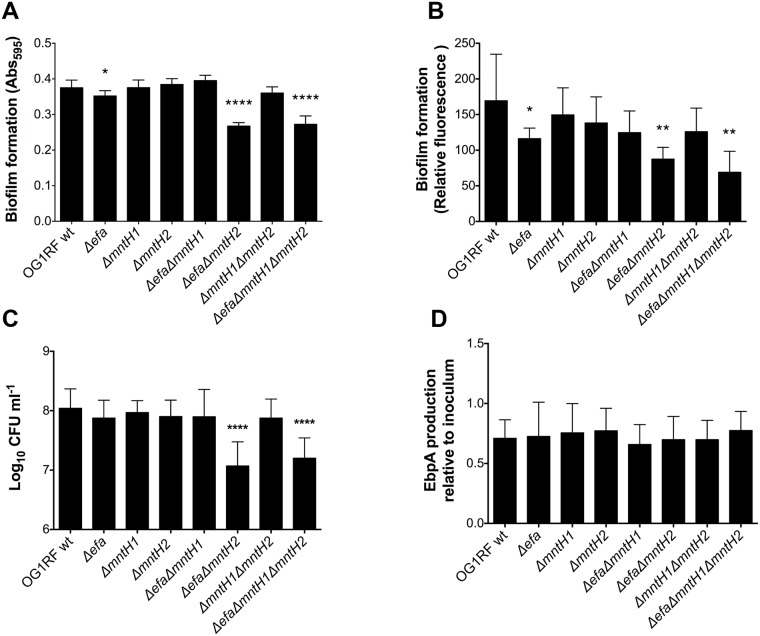
Fig 9. High-affinity Mn acquisition promotes biofilm formation in urine.
(A-B) Fibrinogen-coated (A) 96-well polystyrene plates or (B) silicone catheters were incubated with E. faecalis strains for 24 hours in human urine supplemented with 20 mg ml-1 BSA. (A) Plates were stained with 0.5% crystal violet, which was dissolved with 33% acetic acid and absorbance at 595 nm was measured. (B) Fixed catheters were incubated with rabbit anti-Streptococcus group D antigen and Odyssey secondary antibody. Biofilm formation was quantified by infrared scanning. (C) Catheters were vortexed and sonicated to retrieve biofilm-associated bacteria and plated for cell enumeration. (D) EbpA expression in urine. Strains were grown in urine + BSA overnight prior to quantification of EbpA by ELISA. EbpA surface expression was detected using mouse anti-EbpAFull and HRP-conjugated goat anti-rabbit antisera, and absorbance was determined at 450 nm. EbpA expression titers were normalized against the bacterial titers. Experiments were performed independently in triplicate per condition and per experiment. Biofilm quantification assays and presence of surface EbpA were analyzed by a two-tailed Mann-Whitney U test. Differences in log10 CFU on catheters were assessed via a one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s post-test (*p ≤ 0.05, ** p ≤ 0.01, **** p ≤ 0.0001).