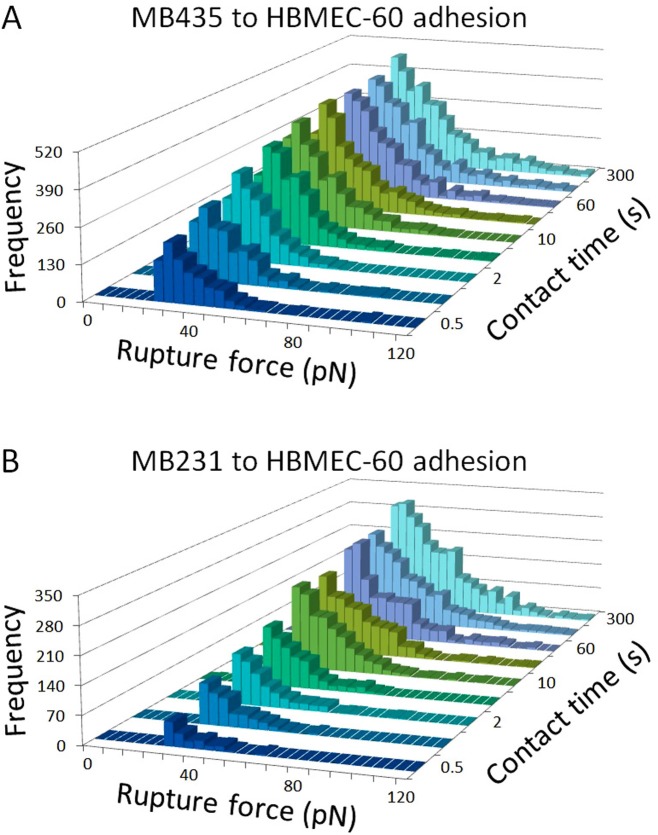
Fig 4. Distributions of rupture forces detected during cancer-HBME adhesion with cell-cell contact times of 0.5, 1, 2, 5, 10, 30, 60, 120 and 300 sec.
Note 3.89-fold increase (from 903 to 3516 counts) in the frequency counts of the detectable rupture events for MB435 and 15.39-fold increase (from 156 to 2401 counts) for MB231 from 0.5 to 300 sec of cell-cell contact. Also note a significant shift of the rupture force frequency distribution histograms to the right for both cancer cell lines. Similar changes in histograms of rupture force distribution for both MB435 (A) and MB231 (B) cells indicate that both the increase in frequencies of individual adhesion events and involvement of stronger ligand-receptor interactions contributed to the change in total adhesion force over time.