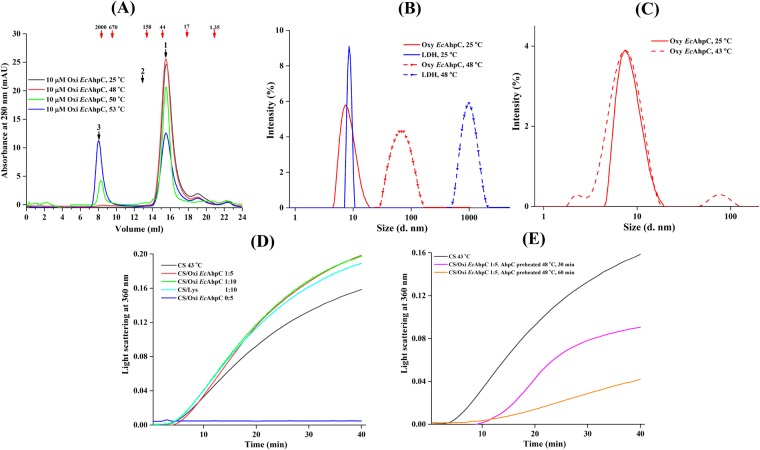
Figure 2.
Heat-shock induced oligomerization of oxidized EcAhpC. (A) SEC elution profile of 10 µM oxidized EcAhpC incubated at 25 °C (black), 48 °C (red), 50 °C (green) and 53 °C (blue). The dimeric (estimated molecular mass of 38 kDa) and decameric (estimated molecular mass of 195 kDa) forms of oxidized EcAhpC elution volumes were denoted as 1 and 2, respectively. A very large shift in the elution volume (denoted as 3) observed for the sample treated with heat indicates HMW oligomers formation with an estimated molecular mass of 2.0–3.0 MDa. The numbers indicated with red arrows in the chromatogram represent the molecular mass (kDa) of standard proteins. (B) DLS measurement of oxidized EcAhpC (red) and LDH (blue) were equilibrated at 25 °C (—) and 48 °C (−) for 10 min, respectively. An increase in mean effective diameter were observed for both the samples at 48 °C for 10 min. (C) DLS studies showed no significant changes in the oligomerization of oxidized EcAhpC (red) after treatment at 43 °C for 10 min (−). (D) Light scattering analysis showed that 0.5 µM of CS aggregated at 43 °C (black) and that the aggregation was not prevented in the presence of 5 µM (red) and 10 µM (green) of oxidized EcAhpC or 10 µM lysozyme (cyan). (E) 0.5 µM CS aggregation at 43 °C was prevented in the presence of 5 µM oxidized EcAhpC, which was pre-heated at 48 °C for 30 (magenta) and 60 (orange) min, respectively.