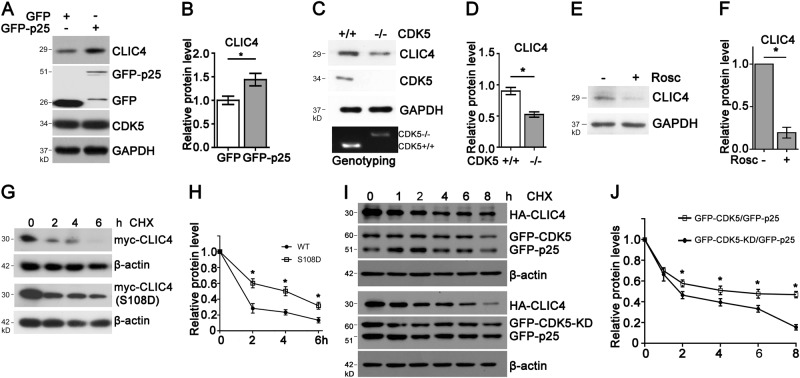
Fig. 4. CDK5 promotes CLIC4 protein stability.
a, b Protein levels of CLIC4 in N2a cells transiently transfected with GFP tag or GFP-p25 for 24 h. Relative CLIC4 levels were quantified in b (n = 3 experiments). c, d CLIC4 and CDK5 protein levels in the brain homogenates of wild-type and CDK5−/− littermate embryos at E16.5. Embryos were genotyped and brain samples were analyzed by western blotting (c). Upper band in the agarose gel indicates CDK5−/− genotype, while lower one means wild-type. Relative CLIC4 levels were quantified in D (n = 3 experiments, 4 embryos each group). e, f Immunoblotting of lysates of primary cortical neurons treated with 5 μM Roscovitine for 24 h. Relative CLIC4 levels were quantified in f (n = 3 experiments). g, h Turnover of myc-CLIC4 and myc-CLIC4 (S108D) in N2a cells treated with 100 μM cycloheximide (CHX) for indicated times. Cell lysates were immunoblotted with anti-myc and anti-β-actin antibodies (g). Normalized myc-tagged CLIC4 proteins levels were quantified in h (n = 3 experiments). i, j Turnover of HA-CLIC4 in N2a cells transiently transfected with HA-CLIC4/GFP-CDK5/GFP-p25 or HA-CLIC4/GFP-CDK5-KD/GFP-p25 and treated with CHX for indicated times. Lysates were subjected to western blotting for HA-tagged and GFP-tagged proteins and β-actin (i). Normalized HA-CLIC4 protein levels were quantified in j (n = 3 experiments). Data are presented as the mean and SEM, and were analyzed by unpaired Student’s t-test (b, d, f) or two-way ANOVA test (h, j). *P < 0.05