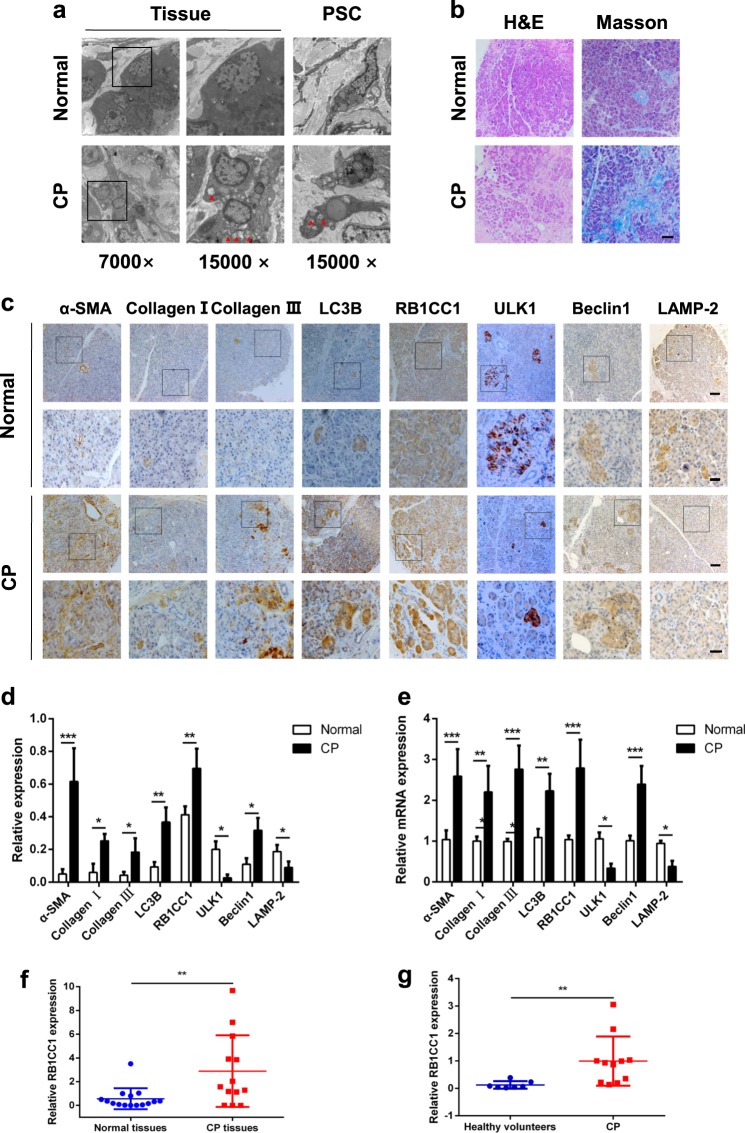
Fig. 6. RB1CC1 expression is correlated with the severity of pancreatic fibrosis in CP patients.
a The TEM assays revealed the autophagic levels in human normal tissues (n = 4) and CP tissues (n = 4), also in human quiescent and activated PSCs (n = 4). b The H&E and Masson assays were assessed to show the formation of fibrosis and collagen in normal tissues (n = 4) and CP tissues (n = 4) (bars = 50μm). c, d The expressions of α-SMA, Collagen I, Collagen III, LC3B, RB1CC1, ULK1, Beclin1, and LAMP-2 were analyzed via immunohistochemistry in normal tissues (n = 4) and CP tissues (n = 4) (bars = 50 μm, original magnification, ×10; bars = 20 μm, original magnification, ×40). The relative expressions of each indicator were analyzed in five high-power fields. e The expressions of α-SMA, Collagen I, Collagen III, LC3B, RB1CC1, ULK1, Beclin1, and LAMP-2 were determined via qRT-PCR assays. The relative expression represents the ratio of target to GAPDH. f The relative mRNA level of RB1CC1 was increased in CP tissues (n = 13) compared with normal tissues (n = 15). g The RB1CC1 mRNA was significantly elevated in plasma of CP patients (n = 11) than that in health individuals (n = 7). Data are expressed as mean ± SD. The results are representative of three independent experiments (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001)