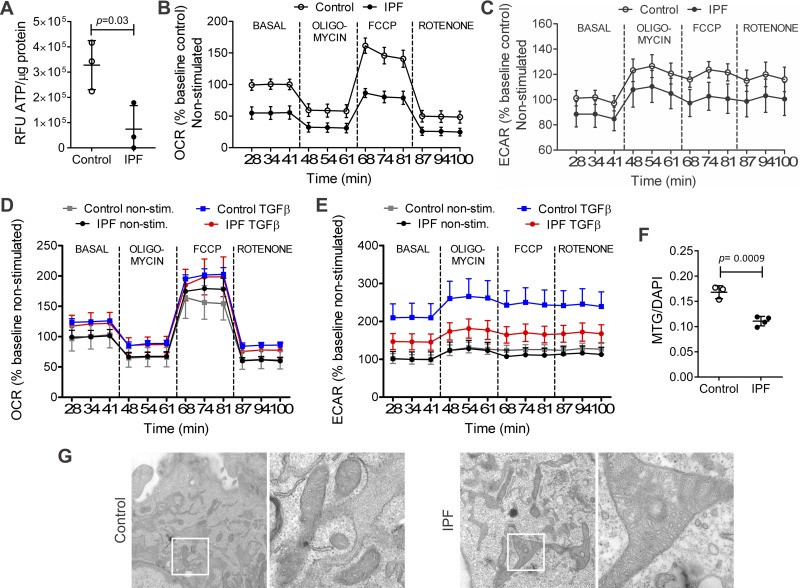
Fig. 3.
Mitochondrial function and structure in hLFs. IPF hLFs show lower energy production (ATP content), lower mitochondrial function measured by oxygen consumption rate (OCR), lower glycolytic flow measured by extracellular acidification rate (ECAR), and altered mitochondrial structure compared with controls. A: basal content of ATP was measured in control and IPF hLFs, showing statistically significant decrease in ATP in IPF hLFs compared with controls. Results were normalized by protein concentration. Bars represent SE (P = 0.03; n = 3 per group). B: OCR bioenergetic profile of nonstimulated control and IPF hLFs showing a significant decrease in basal and maximal respiration in IPF hLFs compared with controls (n = 3 per group; P = 0.001). C: %baseline ECAR of nonstimulated control and IPF hLFs showing no differences in glycolysis across the bio profile in IPF hLFs compared with controls (n = 3 per group. P = 0.2). D: OCR bioenergetic profile of TGFβ stimulated hLFs, showing no differences upon TGF-β (n = 3 in control and n = 4 in IPF group; P = 0.12). E: %baseline ECAR of TGF-β stimulated control and IPF hLFs showing a significant decrease in glycolysis in IPF hLFs compared with controls (n = 3 in control and 4 in IPF hLFs; P < 0.001). F: mitochondrial mass using MitoTracker green/DAPI (n = 3 control hLFs and 4 IPF hLFs). Bars represent SE. G: representative image of electronic microscopy of control and IPF hLFs at ×25 and ×100 magnification camera showing mitochondrial structure. For detailed statistical analysis of figures B to E, refer to Tables 3–5.