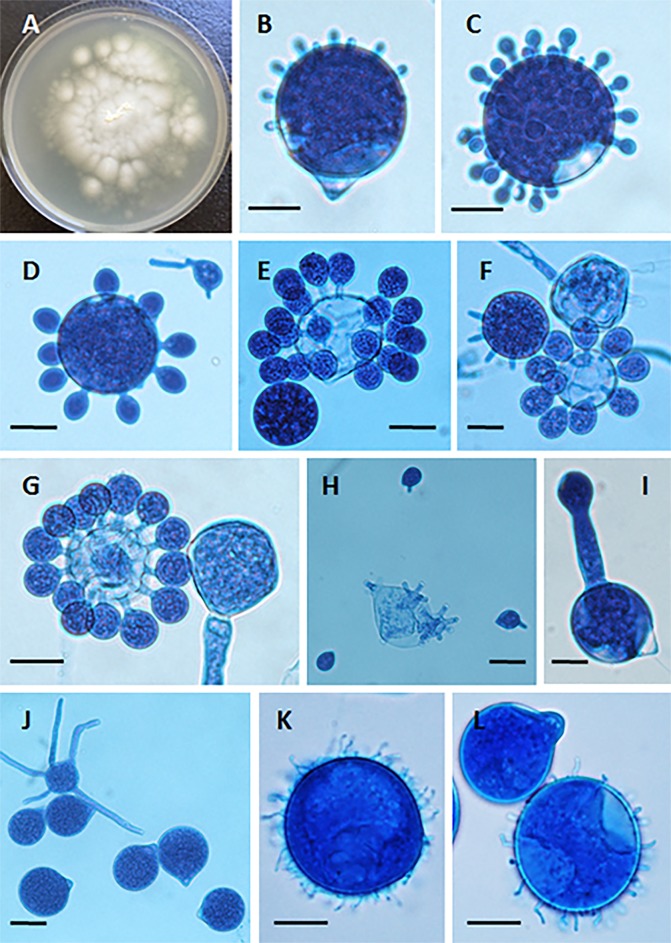
FIG 2.
(A) Yellow-white colony of Conidiobolus coronatus on 2% Sabouraud dextrose agar (SDA) from a primary culture after 48 h. The presence of a few aerial hyphae and satellite colonies due to the ejection of conidia from sporangiophores, detected on the lid of the SDA plate (data not shown), is also observed. (B to G) Formation of secondary conidia from a primary multinucleate conidium of C. coronatus in lactophenol blue. Bars, 20 μm (B, D, and G), 22 μm (C and E), and 21 μm (F). Note the different steps of development into fully formed corona secondary conidia in panels F and G. (H) Ejected secondary conidia and also several empty sporangiophores and three small ejected secondary conidia, some of which are developing germ tubes. Bar, 22 μm. (I and J) Single conidiophore with a secondary sporangiophore and conidium (I) and several primary C. coronatus conidia, one with several coenocytic hyphae (J). Bars, 20.0 μm (I) and 22 μm (J). (K and L) Presence of C. coronatus villose conidia in water agar cultures. Bars, 18 μm (K) and 19 μm (L).