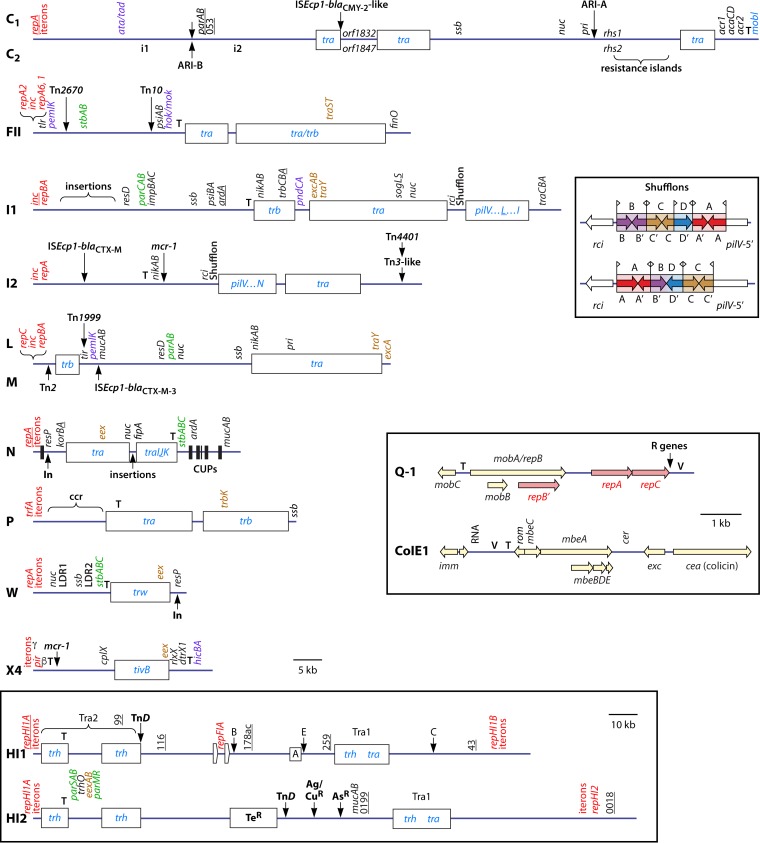
FIG 5.
Representative diagrams of the backbone organization of major plasmid types associated with antibiotic resistance in Enterobacteriaceae. Plasmid types are indicated on the left. Diagrams are approximately to scale, with those in boxes at a different scale (see scale bars). Selected genes/gene regions involved in various functions are shown by the following colors: red, replication/oriV; blue, conjugation; green, maintenance; brown, entry exclusion; and purple, TA. Additional features may be shown for different plasmid types, with most explained further in the text, except for the following: ssb, single-stranded DNA binding protein gene; pri/sog, primase gene; resD/resP, resolvase gene; stb, stability/partitioning gene; psiAB, plasmid SOS inhibition gene; impABC/mucAB, mutagenic DNA polymerase gene; ardA, antirestriction gene; korAB, kill override gene (involved in regulation of tra); ccr, central control region; LDR, long direct repeats. Origins of transfer (oriT) are indicated by “T,” if they have been defined. Insertion points for resistance regions common to plasmids of the same type are also indicated, in some cases, by labeled vertical arrows. C backbones are represented by a single line, with differences (presence/absence of ARI-A, orf1832 versus orf1847, rhs1 versus rhs2, and presence/absence of i1 and i2) shown above (C1) and below (C2). L and M backbones are also represented by a single line, with different insertions in common plasmids shown above (L) and below (M) (modified versions of Tn2 with additional resistance genes are also found at the site indicated for Tn2). These two plasmid types differ mainly in traY/excA (entry exclusion) and traX (relaxase), with differences in inc distinguishing the M1 and M2 types. For HI1 plasmids, the type 1 backbone is shown, with insertions found in type 2 plasmids indicated above (A to E; region D from reference 211 was recognized as a transposon, TnD, in reference 208). Insertions that give resistance to various heavy metals are indicated as follows; Te, tellurite; Ag, silver; Cu, copper; and As, arsenic. Targets for pMLST schemes are underlined (for C plasmids, repA, parA, parB, and 053; for I1 plasmids, repA, ardA, trbA, sogS, and pilL; for N plasmids, repA, korA, and traJ; for HI1 plasmids, repA [HCM1.64] as well as HCM1.99, HCM1.116, HCM1.178ac, HCM1.259, and HCM143 [abbreviated “99,” etc.]; and for HI2 plasmids, 0199 and 0018). Shufflons in I1 plasmid R64 (above) and I2 plasmid R721 (below) are shown in a separate box. Segment A contains partial open reading frames A and A′, etc. sfx repeats are represented by flags. Diagrams are based on information in previous publications and/or sequences from INSDC accession numbers for prototype plasmids, as follows: C1 and C2, references 181 and 193; FII, accession number AP000342; I1, references 55 and 514; I2, reference 236 and accession number KP347127; I1 and I2 shufflons, reference 493; L/M, references 239, 245, and 515; N, reference 250 and accession number AY046276; P, reference 260 and accession number U67194; W, reference 280 and accession number BR000038; X, reference 298; HI1, references 205, 208, and 211 and accession numbers AF250878 and AL513383; HI2, references 205 and 213 and accession number BX664015; Q-1, reference 307; and ColE1, reference 311 and accession number J01566.