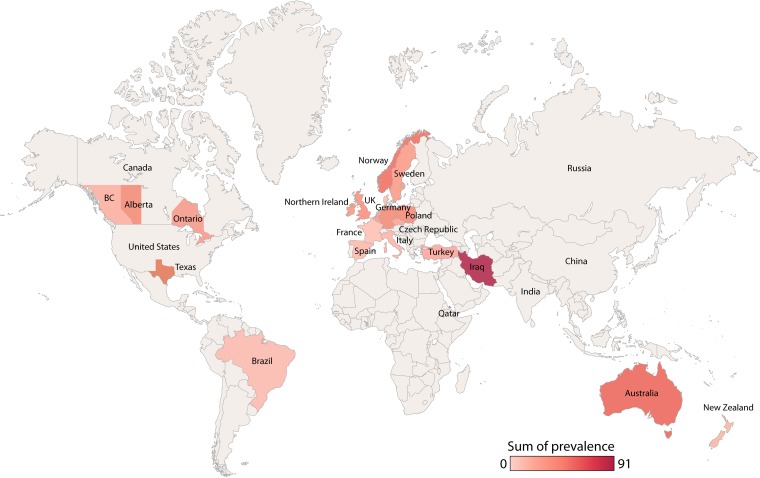
FIG 4.
Global prevalence of clonal P. aeruginosa strains. This map is, however, limited. In many cases, a single center's data are extrapolated to an entire country, and admittedly, rates of shared clonal strains have been shown to be highly clinic dependent. Furthermore, rates reported here are from aggregates of the most recently available data. As rates of clonal strain prevalence may change over time, what was once true may no longer be the case. Whereas newer studies have employed technologies such as MLST and VNTR, enabling investigators of individual studies to directly comment on the prevalence of this organism in distant CF populations as well as in non-CF infections and environmental samples, older studies typically used noncomparative genotyping technologies.