Fig. 4.
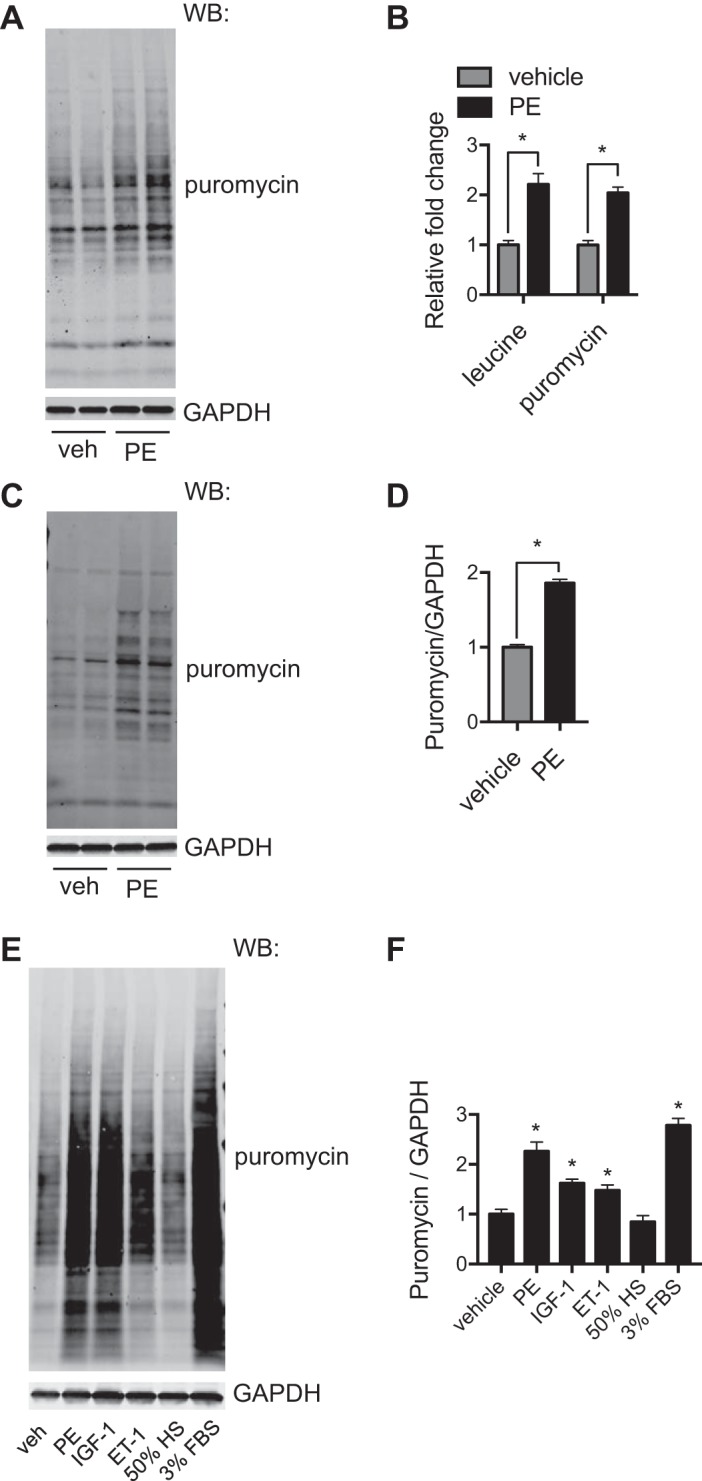
Comparison of the puromycin (puro) method with the radioactive amino acid labeling assay. A: puromycin incorporation under the hypertrophic growth condition. Neonatal rat ventricular myocytes (NRVMs) were treated with phenylephrine (PE) for 24 h. At the last 2 h, puromycin was included, and cellular lysates were subjected to immunoblot analysis. B: NRVMs with the same treatment condition were used for [3H]leucine labeling. Comparison between these two methods showed similar increases after PE treatment. We conclude that the puromycin method is equally sensitive compared with the conventional radioactive amino acid labeling approach. C: puromycin labeling was used to monitor hypertrophic growth in adult mouse ventricular myocytes (AMVMs). Here, AMVMs were treated by PE for 24 h. Puromycin was introduced at the last hour of treatment. Protein lysates were used for immunoblot analysis. D: quantification showed that PE induced significant hypertrophy in AMVMs. E: puromycin labeling was conducted to examine hypertrophic effects of different stimuli. NRVMs were subjected to various treatments and puromycin incorporation, which were later visualized by immunoblot analysis. F: quantification of the puromycin signal over controls showed significant increases in puromycin incorporation in most hypertrophic treatments. WB, Western blot analysis; veh, vehicle; IGF-1, insulin-like growth factor 1; ET-1, endothelin-1; HS, hyposmotic solution. n = 3–4/group. *P < 0.05.
