Fig. 1.
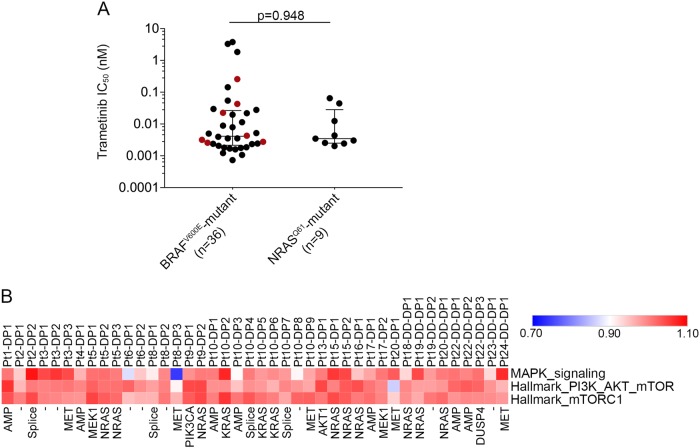
Activation of PI3K by RAS mutations does not diminish sensitivity of melanoma cells to MEK inhibition. a Trametinib sensitivity data (IC50 values) derived from the Genomics of Drug Sensitivity in Cancer database comparing BRAFV600E-mutant and NRASQ61-mutant melanoma cell lines. Data highlighted in red indicate BRAFV600E-mutant cells with concurrent loss of function NF1, PTEN mutations or the activating NRASQ61K mutation. The sensitivity of these cells (red points) were not significantly different from the other BRAFV600E mutant melanoma cells (data highlighted in black, Mann–Whitney p = 0.410). Two-tailed Mann–Whitney test was used to determine differences between BRAF and NRAS mutant melanoma populations (p = 0.948). Median and interquartile ranges are shown on the scatter plot. b Heat map showing ssGSEA ratio scores of MAPK32, PI3K and mTORC signalling activity in 42 PROG melanomas relative to their matched PRE tumours. The main resistance mechanism is shown below each PROG tumour. Data are derived from4,5,16,33 and tumour samples labelled according to16. DP single-drug (BRAF inhibitor) PROG tumours, DD-DP double-drug (combination BRAF and MEK inhibitor) PROG tumours. AMP BRAF amplification, splice BRAF-splice variant, - unknown mechanism of resistance