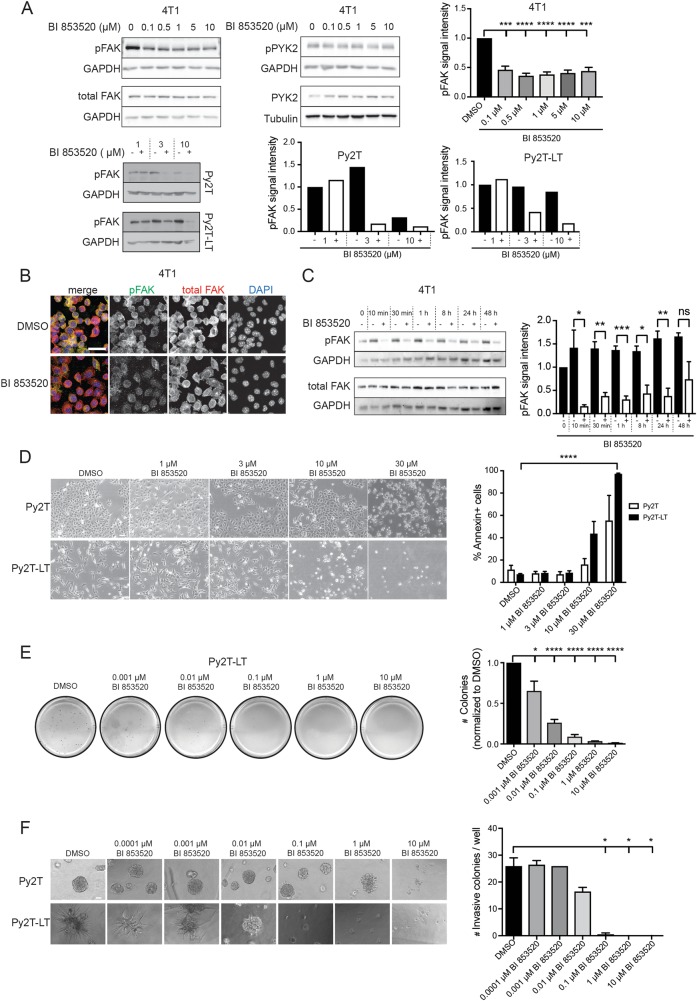
Fig. 1. BI 853520 decreases Y397-FAK phosphorylation in a dose-dependent and time-dependent manner.
a To determine the effective dose of BI 853520, 4T1, Py2T, and Py2T-LT cells were exposed to increasing concentrations of BI 853520 (0, 0.1, 0.5, 1, 5, and 10 µM for 4T1 cells; 1, 3, and 10 µM for Py2T and Py2T-LT cells) for 24 h. Top left panel: 4T1 cell lysates were examined by immunoblotting analysis for phospho-FAK-Y397 (pFAK) and total FAK (FAK). GAPDH served as a loading control (n = 4). Immunoblotting for phospho-PYK2-Y402 (pPYK2), total PYK2 (PYK2), and GAPDH and tubulin as loading control is shown in the top middle panel (n = 2). Top right panel: Quantification of pFAK signal intensity normalized to GAPDH and total FAK/GAPDH ratios from the immunoblotting analysis shown on the left. Statistical analysis was performed using an unpaired, two-tailed Student’s t test. ****p < 0.0001, ***p < 0.001. Bottom left panel: Py2T and Py2T-LT cell lysates were examined by immunoblotting analysis for phospho-FAK-Y397 (pFAK). GAPDH served as a loading control (n = 1). Right panel: Quantification of pFAK signal intensity normalized to GAPDH from the immunoblotting analysis shown on the left. b 4T1 cells grown on coverslips were treated with the effective dose of BI 853520 (0.1 µM) for 96 h, followed by immunofluorescence staining for pFAK (Y397, green), total FAK (red), and DNA (blue). Images were obtained using a laser-scanning confocal microscope Leica SP5 (n = 2). Scale bar, 30 µm. c To determine the onset and duration of BI 853520-mediated pFAK downregulation, 4T1 cells were treated for the times indicated with 0.1 µM BI 853520. Cell lysates were analyzed by immunoblotting for pFAK (Y397), total FAK, and GAPDH as a loading control (n = 3). Right panel: Quantification of pFAK signal intensity normalized to GAPDH and total FAK/GAPDH ratios from the immunoblotting analysis shown on the left. Statistical analysis was performed using an unpaired, two-tailed Student’s t test. ***p < 0.001, **p < 0.01, and *p < 0.05. d Cytotoxic effects of high doses of BI 853520 on murine breast cancer cells cultured on plastic surface. Epithelial Py2T and mesenchymal Py2T-LT murine breast cancer cells were treated with BI 853520 at the concentrations indicated and phase contrast micrographs were taken. Cells were then suspended, and staining for Annexin-V as marker of apoptosis was quantified by flow cytometry (n = 2). Statistical analysis was performed using an unpaired, two-tailed Student’s t test. ****p < 0.0001. Scale bar: 120 μM. e BI 853520 represses colony formation in three-dimensional growth conditions. Py2T-LT cells were seeded in soft agar gels and treated with increasing concentrations of BI 853520 as indicated. The numbers of colonies were quantified. (n = 3). Unpaired, two-tailed Student’s t test. ****p < 0.0001, *p < 0.05. f BI 853520 represses mesenchymal murine breast cancer cell invasion cultured in Matrigel. Epithelial Py2T and mesenchymal Py2T-LT murine breast cancer cells were seeded in Matrigel and treated with increasing concentrations of BI 853520 as indicated. Phase contrast microscopy pictures were taken and the numbers of invasive colonies were quantified. Epithelial Py2T cells formed differentiated spheres which only responded to BI 853520 at high, toxic concentrations (n = 1). Statistical analysis was performed using an unpaired, two-tailed Student’s t test. *p < 0.05. Scale bar: 60 μM. ns not significant