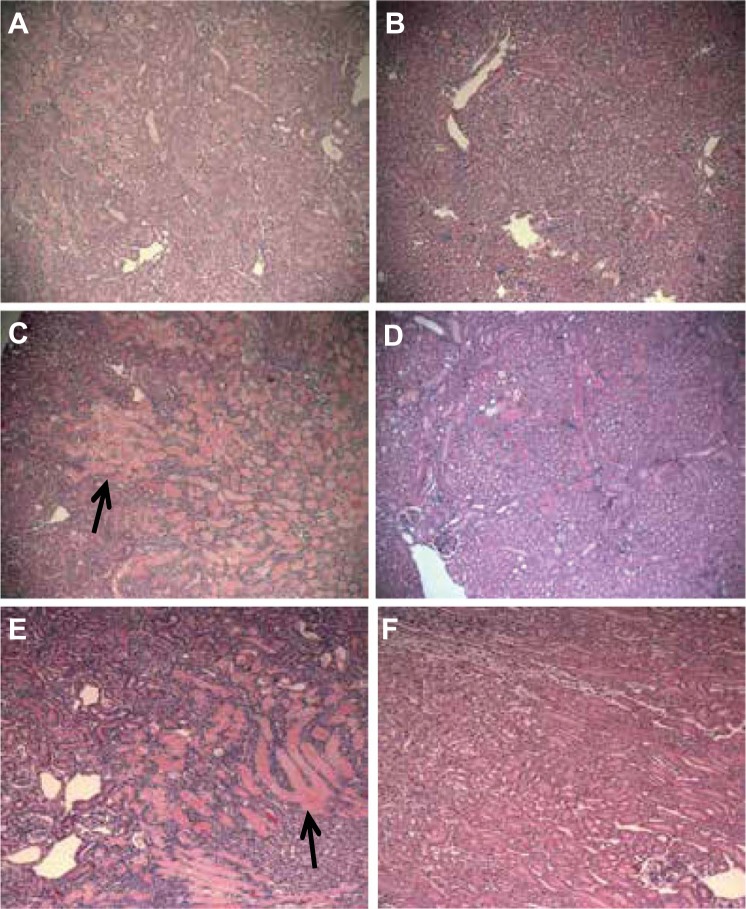
Fig. 1.
Acute tubular injury (ATI) in mouse cortical tissue sections 48 h after ischemia-reperfusion (I/R) injury. A: untreated wild-type (WT) mice showed 40–50% of cortical tissue with diffuse acute tubular injury (tubules with pink casts). B: macrophage migration inhibitory factor-like protein (MIF-2/D-DT) treatment markedly decreased the extend and severity of damaged proximal tubule tissue in WT mice. C: Mif−/− mice showed 70–90% of cortical tissue with severe tubular injury and extensive intraluminal cast formation (black arrow). D: injection of MIF-2/D-DT dramatically ameliorated the degree of ATI in Mif−/− mice. E: Mif-2−/− mice showed an even more severe degree of tubular injury (95% of cortex) with extensive cast formation (black arrow). F: MIF-2/D-DT injections reduced the extend and severity of the tubular injury by 70% in Mif-2−/− mice. A–F: hematoxylin and eosin: ×40. All animal groups (sham or I/R) contained 6–8 animals.