Fig 3.
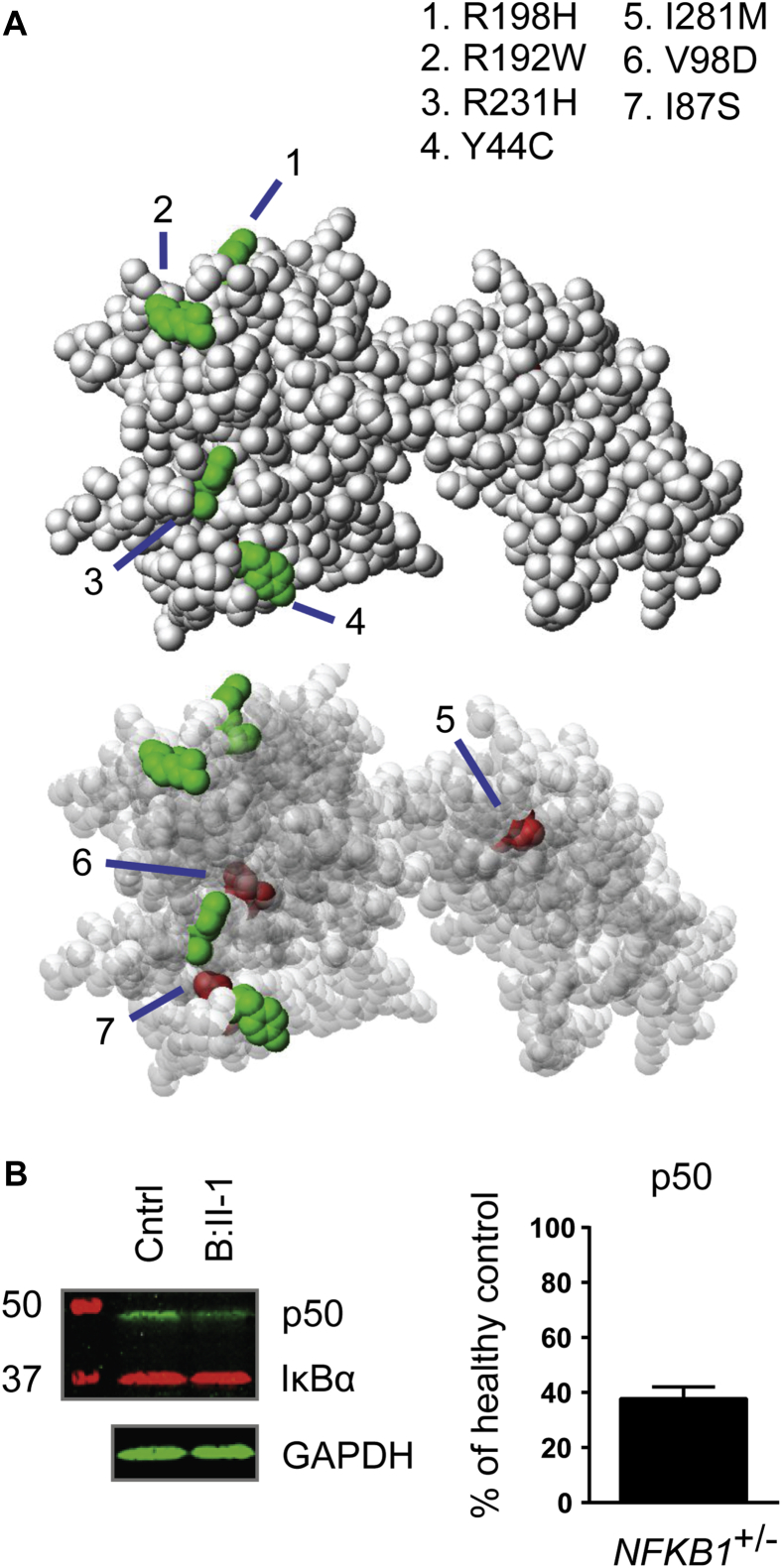
NFKB1 LOF variants lead to haploinsufficiency of the p50 protein. A, Localization of RHD substitutions with a high Combined Annotation Dependent Depletion (CADD) score (>20) within the structure of the NF-κB p50 monomer. Shown is a solid (top panel) and a transparent (bottom panel) sphere representation of the NF-κB p50 monomer. Perturbed residues indicated in green were observed in a control data set and are located on the outside of the structure, whereas residues shown in red were perturbed exclusively in the PID cohort and are buried inside the structure. B, Western blot analysis targeting p50, IκBα, and glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) of NFKB1 variant carriers. Left, Representative blot of a healthy control subject and patient B-II:1; right, summary of 16 NFKB1 variant carriers showing haploinsufficiency expressed as a percentage of healthy control subjects on the same blot corrected for GAPDH (mean ± SEM).