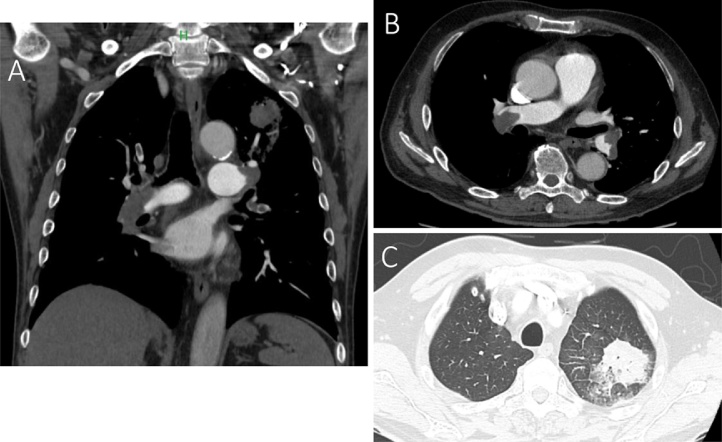
Fig. 1.
Coronal (A) and horizontal (B, C) section of contrast-enhanced computed tomography imaging at the time of admission. There were massive thrombi in both branches of the main pulmonary artery, and there was also a patchy area of consolidation in the upper lobe of the left lung, which appeared to be caused by the pulmonary infarction.