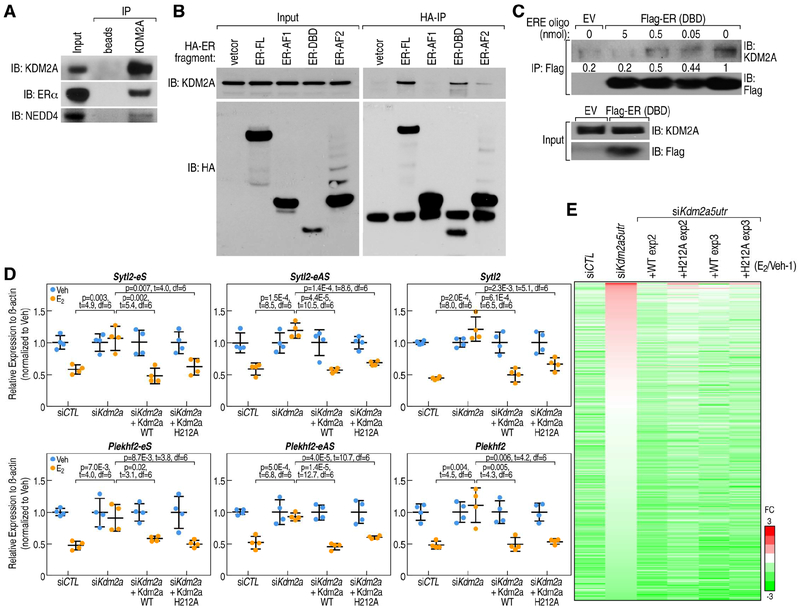
Figure 6. KDM2A mediates enhancer decommissioning through its interaction with ERα DNA binding domain.
A, KDM2A interactions with ERα and NEDD4 are revealed by anti-KDM2A antibody (Santa Cruz, H120) co-immunoprecipitation in MCF7 cells under E2 treatment. B, The interaction of ERα with KDM2A is dependent on its DNA-binding domain (DBD), as shown by coimmunoprecipitation using HA-tagged ERα fragments. KDM2A interacts with full length of ERα (ER-FL) and ERα DNA-binding domain (ER-DBD), but not with ERα AF1 domain (ER-AF1). C, In vitro immunoprecipitation of KDM2A with Flag-tagged ERα DBD (Flag-ER DBD) protein, in presence of 0, 0.5, 5 and 50 μl 2xERE oligonucleotides (100 μM) as competitor. The interaction between KDM2A and ERα DBD was quantitatively decreased by DNA oligos encompassing an ERE motif. Empty vector (EV), which does not express Flag-tagged ERα DBD protein, served as a control. D, RT-qPCR showing expression levels of Sytl2-enhancer, Plekhf2-enhancer and their target gene repression by E2 treatment can be rescued by both wild type KDM2A and H212A mutated KDM2A (eS: eRNA sense chain; eAS: eRNA anti-sense chain). Data are presented as mean ± s.d. P values denote differences between each group upon E2 treatment are shown (N = 4; unpaired t test). E, Heatmap showing that eRNA expression levels were decreased by E2 in siCTL condition, and this was reversed by the knockdown of Kdm2a (by siKdm2a5utr); the effect of siKdm2a5utr could be rescued by either wild type or H212A mutant HA-tagged KDM2A in MCF7 cells. The relative fold-changes (E2/Veh-1) of each enhancer are shown.