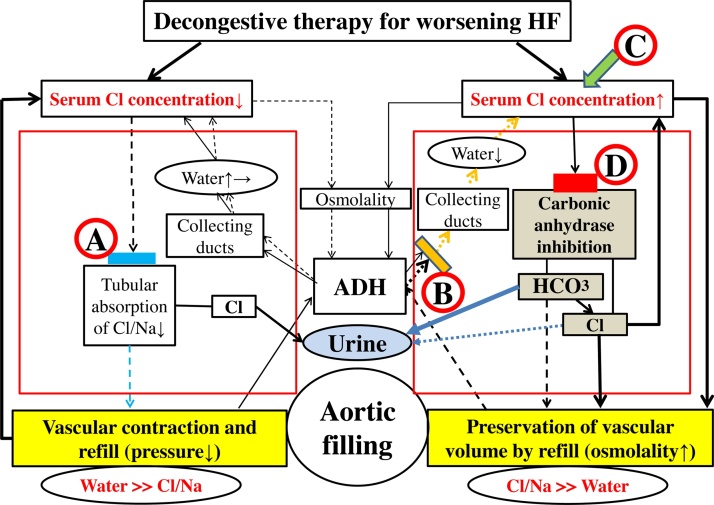
Fig. 1.
Heart failure treatment and resolution of worsening HF based on the “chloride theory”; conventional diuretic therapy ( ), V2-receptor antagonist (
), V2-receptor antagonist ( ), chloride supplementation (
), chloride supplementation ( ), and carbonic anhydrase inhibitor (
), and carbonic anhydrase inhibitor ( ). Blue and yellow blocks represent inhibition of the absorption of chloride/sodium and water in each. Red block indicates the action of carbonic anhydrase inhibition by acetazolamide. Therapeutic effect induced by each treatment is shown by a solid or dotted line. Solid line indicates enhanced supply or excitatory effect, and dotted line indicates reduced supply or inhibitory effect. Different effect strengths are expressed by the thickness of each line. Large red square represents the kidney as an active place of the reabsorption of electrolytes and water.
). Blue and yellow blocks represent inhibition of the absorption of chloride/sodium and water in each. Red block indicates the action of carbonic anhydrase inhibition by acetazolamide. Therapeutic effect induced by each treatment is shown by a solid or dotted line. Solid line indicates enhanced supply or excitatory effect, and dotted line indicates reduced supply or inhibitory effect. Different effect strengths are expressed by the thickness of each line. Large red square represents the kidney as an active place of the reabsorption of electrolytes and water.
ADH, antidiuretic hormone; Cl, chloride; HCO3−, bicarbonate; HF, heart failure; Na, sodium.