Figure 1.
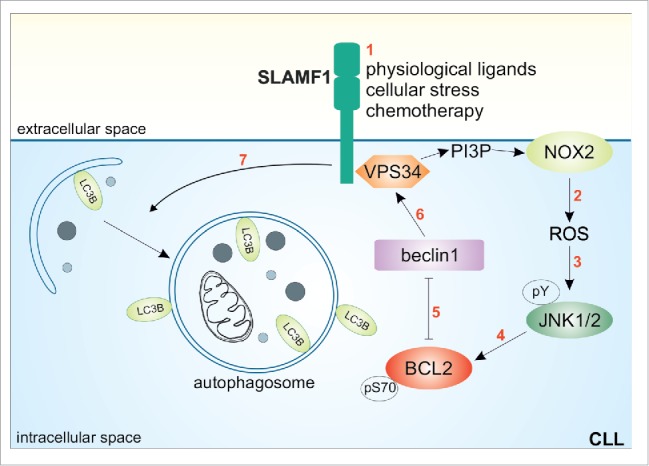
Molecular mechanism of SLAMF1-induced autophagy in CLL cells. Upon activation (1), SLAMF1 initiates a signaling pathway that increases NOX2-mediated reactive oxygen species (ROS) production (2), which is in turn responsible for JNK1/2 tyrosine phosphorylation (3). JNK1/2 then phosphorylates BCL2 at serine 70 (4), causing its dissociation from beclin 1 and leaving it free to assemble the autophagic complex including VPS34 and SLAMF1 itself. As a consequence, autophagosome formation is induced (7), leading to execution of autophagy.
