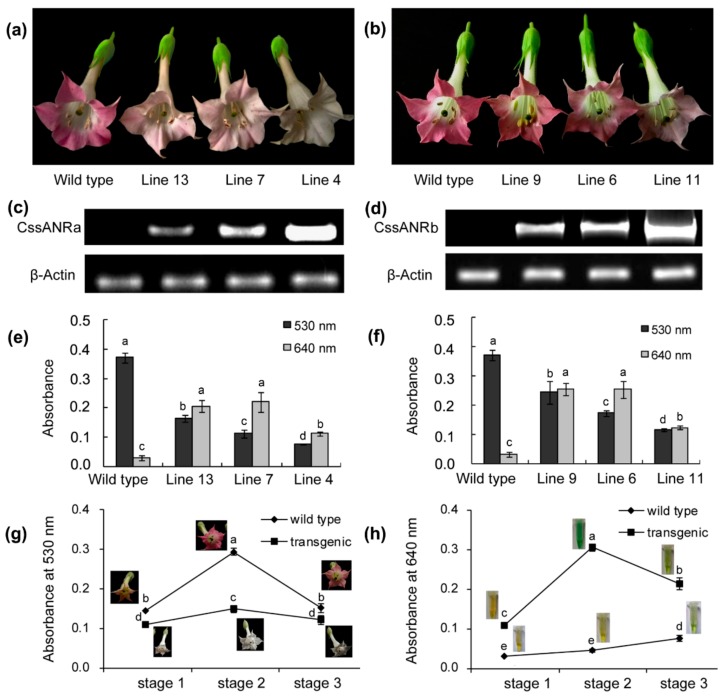
Figure 7.
Ectopic expression of CssANRa and CssANRb genes in tobacco flowers. (a,b) pigmentation phenotypes of CssANRa (a, three lines) and CssANRb (b, three lines) transgenic vs. wild-type tobacco flowers fully opened, (c,d) gel images showing expression of CssANRa (c) and CssANRb (d) transgene fragments amplified from fully opened flowers by semi-quantitative PCR; (e) anthocyanin and PA levels in CssANRa transgenic vs. wild-type flowers estimated at 530 nm and 640 nm, respectively; (f) anthocyanin and PA levels in CssANRb transgenic vs. wild-type flowers estimated at 530 nm and 640 nm, respectively; (g,h) dynamic patterns of anthocyanins (g) and PAs (h) levels at three selected development stages of CssANRa transgenic flowers. In (e,f), bars labeled with different low case letters for anthocyanin or PAs mean significant difference (p-value less than 0.05), while with the same ones mean insignificance (p-value higher than 0.05). In (g,h), points labeled with different low case letters mean significant difference (p-value less than 0.05), while with the same ones mean insignificance (p-value higher than 0.05). p-Values were calculated with Student’s t-test.