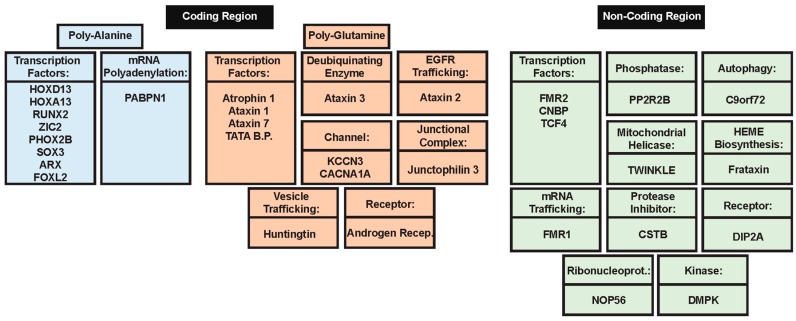
Figure 1.
Major known functions of proteins with pathogenic repeat expansions. Proteins with pathogenic expansions have varied functions depending on the type of expansion present. Poly-alanine (poly-Ala) expansions have the least variability in functions, with 8 of the 9 engaging in some sort of transcription regulation. Poly-glutamine (polyQ) expansions that cause pathology have more varied functions, but the majority participate in transcription regulation as well. Pathogenic repeats in non-coding regions occur in genes encoding proteins with the most varied functions. They include everything from catalytic proteins to receptors. Since the repeat extension occurs in the non-coding region of the gene, it is conceivable that there are not more synonymous functions among pathogenic repeat proteins in non-coding regions.