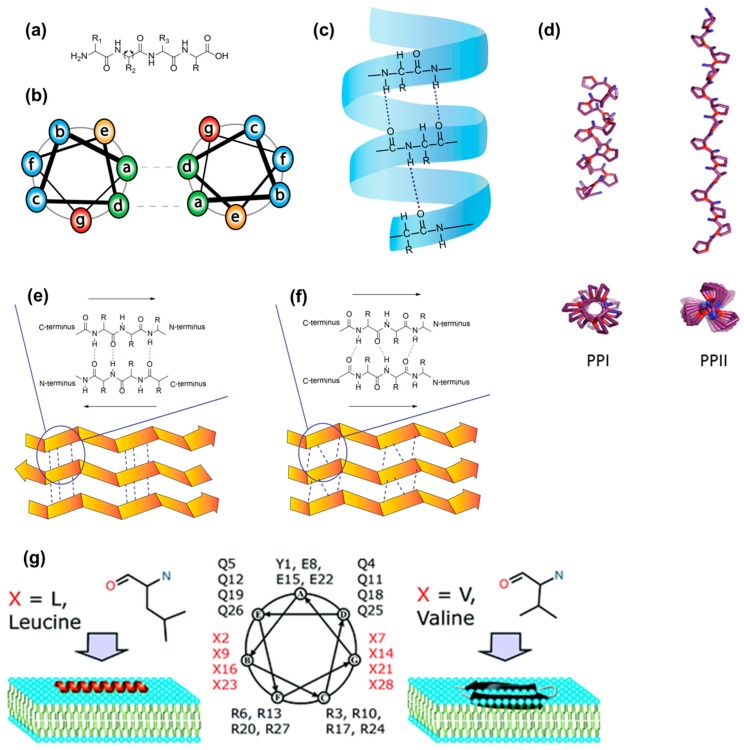
Figure 5.
Schematic representation of (a) primary peptide sequence with dihedral angles; (b) heptad units: (abcdefg)n where the a and d (green) are hydrophobic amino acids, e and g (orange and red) are oppositely charged amino acid residues, and b, c and f (blue) represent the solvent-exposed amino acids; (c) α-helix structure indicating hydrogen bonding; (d) Structures of PPI and PPII reprinted with permission from reference [113] (Copyright © 2017, American Chemical Society); schematic representation of (e) anti-parallel and (f) parallel β-sheets found in proteins and synthetic peptides. (g) Schematic representation α-helical or β-sheet folds that form upon the interaction of CPPs with membranes, where even small changes in the primary sequence result in different folding behavior, reproduced with permission from reference [112] (Copyright © 2010, American Chemical Society).